Petrochemical

Petrochemical plant in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Petrochemicals (also known as petroleum distillates) are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn, palm fruit or sugar cane.
The two most common petrochemical classes are olefins (including ethylene and propylene) and aromatics (including benzene, toluene and xylene isomers).
Oil refineries produce olefins and aromatics by fluid catalytic cracking of petroleum fractions. Chemical plants produce olefins by steam cracking of natural gas liquids like ethane and propane. Aromatics are produced by catalytic reforming of naphtha. Olefins and aromatics are the building-blocks for a wide range of materials such as solvents, detergents, and adhesives. Olefins are the basis for polymers and oligomers used in plastics, resins, fibers, elastomers, lubricants, and gels.[1][2]
Global ethylene and propylene production are about 115 million tonnes and 70 million tonnes per annum, respectively. Aromatics production is approximately 70 million tonnes. The largest petrochemical industries are located in the USA and Western Europe; however, major growth in new production capacity is in the Middle East and Asia. There is substantial inter-regional petrochemical trade.
Primary petrochemicals are divided into three groups depending on their chemical structure:
Olefins includes Ethene, Propene, Butenes and butadiene. Ethylene and propylene are important sources of industrial chemicals and plastics products. Butadiene is used in making synthetic rubber.
Aromatics includes Benzene, toluene and xylenes, as a whole referred to as BTX and primarily obtained from petroleum refineries by extraction from the reformate produced in catalytic reformers using Naphtha obtained from petroleum refineries. Benzene is a raw material for dyes and synthetic detergents, and benzene and toluene for isocyanates MDI and TDI used in making polyurethanes. Manufacturers use xylenes to produce plastics and synthetic fibers.
Synthesis gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen used to make ammonia and methanol. Ammonia is used to make the fertilizer urea and methanol is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate. Steam crackers are not to be confused with steam reforming plants used to produce hydrogen and ammonia.
Methane, ethane, propane and butanes obtained primarily from natural gas processing plants.
Methanol and formaldehyde.
In 2007, the amounts of ethylene and propylene produced in steam crackers were about 115 Mt (megatonnes) and 70 Mt, respectively.[3] The output ethylene capacity of large steam crackers ranged up to as much as 1.0 – 1.5 Mt per year.[4]
The adjacent diagram schematically depicts the major hydrocarbon sources used in producing petrochemicals are.[1][2][5][6]
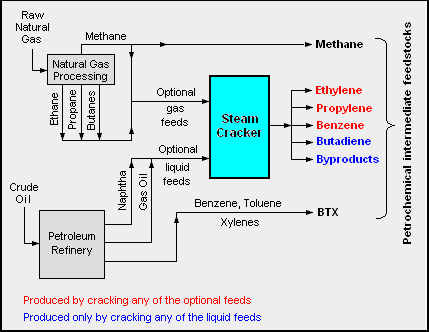
Petrochemical feedstock sources
Like commodity chemicals, petrochemicals are made on a very large scale. Petrochemical manufacturing units differ from commodity chemical plants in that they often produce a number of related products. Compare this with specialty chemical and fine chemical manufacture where products are made in discrete batch processes.
Petrochemicals are predominantly made in a few manufacturing locations around the world, for example in Jubail & Yanbu Industrial Cities in Saudi Arabia, Texas & Louisiana in the US, in Teesside in the Northeast of England in the United Kingdom, in Rotterdam in the Netherlands, and in Jamnagar & Dahej in Gujarat, India. Not all of the petrochemical or commodity chemical materials produced by the chemical industry are made in one single location but groups of related materials are often made in adjacent manufacturing plants to induce industrial symbiosis as well as material and utility efficiency and other economies of scale. This is known in chemical engineering terminology as integrated manufacturing. Speciality and fine chemical companies are sometimes found in similar manufacturing locations as petrochemicals but, in most cases, they do not need the same level of large scale infrastructure (e.g., pipelines, storage, ports and power, etc.) and therefore can be found in multi-sector business parks.
The large scale petrochemical manufacturing locations have clusters of manufacturing units that share utilities and large scale infrastructure such as power stations, storage tanks, port facilities, road and rail terminals. In the United Kingdom for example, there are 4 main locations for such manufacturing: near the River Mersey in Northwest England, on the Humber on the East coast of Yorkshire, in Grangemouth near the Firth of Forth in Scotland and in Teesside as part of the Northeast of England Process Industry Cluster (NEPIC). To demonstrate the clustering and integration, some 50% of the United Kingdom's petrochemical and commodity chemicals are produced by the NEPIC industry cluster companies in Teesside.
Contents
1 History
2 Olefins
3 Aromatics
4 List of petrochemicals
5 See also
6 References
7 External links
History
In 1835, Henri Victor Regnault, a French chemist left vinyl chloride in the sun and found white solid at the bottom of the flask which was polyvinyl chloride. In 1839 Eduard Simon, discovered polystyrene by accident by distilling storax. In 1856, William Henry Perkin discovered the first synthetic dye, Mauveine. In 1888, Friedrich Reinitzer, an Austrian plant scientist observed cholesteryl benzoate had two different melting points. In 1909, Leo Hendrik Baekeland invented bakelite made from phenol and formaldehyde. In 1928 synthetic fuels invented using Fischer-Tropsch process. In 1929, Walter Bock invented synthetic rubber Buna-S which is made up of styrene and butadiene and used to make car tires. In 1933, Otto Röhm polymerized the first acrylic glass methyl methacrylate. In 1935, Michael Perrin invented polyethylene. After World War II, polypropylene was discovered in the early 1950s. In 1937, Wallace Hume Carothers invented nylon. In 1946, he invented Polyester. polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are made from ethylene and paraxylene. In 1938, Otto Bayer invented polyurethane. In 1941, Roy Plunkett invented Teflon. In 1949, Fritz Stastny turned polystyrene into foam. In 1965, Stephanie Kwolek invented Kevlar.[7]
Olefins
The following is a partial list of the major[according to whom?] commercial petrochemicals and their derivatives:

Chemicals produced from ethylene
ethylene – the simplest olefin; used as a chemical feedstock and ripening stimulant
polyethylene – polymerized ethylene; LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE
ethanol – via ethylene hydration (chemical reaction adding water) of ethylene
ethylene oxide – via ethylene oxidation
ethylene glycol – via ethylene oxide hydration
engine coolant – ethylene glycol, water and inhibitor mixture
polyesters – any of several polymers with ester linkages in the main chain
glycol ethers – via glycol condescension- ethoxylates
- vinyl acetate
1,2-dichloroethane- trichloroethylene
tetrachloroethylene – also called perchloroethylene; used as a dry cleaning solvent and degreaser
vinyl chloride – monomer for polyvinyl chloride
polyvinyl chloride (PVC) – type of plastic used for piping, tubing, other things

Chemicals produced from propylene
propylene – used as a monomer and a chemical feedstock
isopropyl alcohol – 2-propanol; often used as a solvent or rubbing alcohol
acrylonitrile – useful as a monomer in forming Orlon, ABS
polypropylene – polymerized propylene
propylene oxide- polyether polyol – used in the production of polyurethanes
propylene glycol – used in engine coolant and aircraft deicer fluid
glycol ethers – from condensation of glycols
acrylic acid- acrylic polymers
allyl chloride –
epichlorohydrin – chloro-oxirane; used in epoxy resin formation
epoxy resins – a type of polymerizing glue from bisphenol A, epichlorohydrin, and some amine
Butene
isomers of butylene – useful as monomers or co-monomers
isobutylene – feed for making methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) or monomer for copolymerization with a low percentage of isoprene to make butyl rubber
1,3-butadiene (or buta-1,3-diene) – a diene often used as a monomer or co-monomer for polymerization to elastomers such as polybutadiene, styrene-butadiene rubber, or a plastic such as acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS)
synthetic rubbers – synthetic elastomers made of any one or more of several petrochemical (usually) monomers such as 1,3-butadiene, styrene, isobutylene, isoprene, chloroprene; elastomeric polymers are often made with a high percentage of conjugated diene monomers such as 1,3-butadiene, isoprene, or chloroprene
higher olefins
polyolefins such poly-alpha-olefins, which are used as lubricants
alpha-olefins – used as monomers, co-monomers, and other chemical precursors. For example, a small amount of 1-hexene can be copolymerized with ethylene into a more flexible form of polyethylene.- other higher olefins
- detergent alcohols
Aromatics

Chemicals produced from benzene
benzene – the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
ethylbenzene – made from benzene and ethylene
styrene made by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene; used as a monomer
polystyrenes – polymers with styrene as a monomer
cumene – isopropylbenzene; a feedstock in the cumene process
phenol – hydroxybenzene; often made by the cumene process
acetone – dimethyl ketone; also often made by the cumene process
bisphenol A – a type of "double" phenol used in polymerization in epoxy resins and making a common type of polycarbonate
epoxy resins – a type of polymerizing glue from bisphenol A, epichlorohydrin, and some amine
polycarbonate – a plastic polymer made from bisphenol A and phosgene (carbonyl dichloride)
solvents – liquids used for dissolving materials; examples often made from petrochemicals include ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, acetone, benzene, toluene, xylenes
cyclohexane – a 6-carbon aliphatic cyclic hydrocarbon sometimes used as a non-polar solvent
adipic acid – a 6-carbon dicarboxylic acid, which can be a precursor used as a co-monomer together with a diamine to form an alternating copolymer form of nylon.
nylons – types of polyamides, some are alternating copolymers formed from copolymerizing dicarboxylic acid or derivatives with diamines
caprolactam – a 6-carbon cyclic amide
nylons – types of polyamides, some are from polymerizing caprolactam
nitrobenzene – can be made by single nitration of benzene
aniline – aminobenzene
methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) – used as a co-monomer with diols or polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or polyamines to form polyureas
alkylbenzene – a general type of aromatic hydrocarbon, which can be used as a presursor for a sulfonate surfactant (detergent)
detergents – often include surfactants types such as alkylbenzenesulfonates and nonylphenol ethoxylates
- chlorobenzene

Chemicals produced from toluene
toluene – methylbenzene; can be a solvent or precursor for other chemicals- benzene
toluene diisocyanate (TDI) – used as co-monomers with polyether polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or polyamines to form polyureas polyurethanes
benzoic acid – carboxybenzene- caprolactam

Chemicals produced from xylenes
mixed xylenes – any of three dimethylbenzene isomers, could be a solvent but more often precursor chemicals
ortho-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form (ortho-)phthalic acid- phthalic anhydride
para-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form terephthalic acid
dimethyl terephthalate – can be copolymerized to form certain polyesters
polyesters – although there can be many types, polyethylene terephthalate is made from petrochemical products and is very widely used.
- purified terephthalic acid – often copolymerized to form polyethylene terephthalate
- polyesters
meta-xylene
isophthalic acid- alkyd resins
- Polyamide Resins
- Unsaturated Polyesters
List of petrochemicals
| Petrochemicals | Fibers | Petroleum | Chemicals |
|---|---|---|---|
Basic Feedstock Benzene Butadiene Ethylene p-Xylene Propylene Intermediates | Acrylic fiber Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) Acrylonitrile styrene (AS) Polybutadiene (PBR) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) Polyethylene (PE) Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) Polyol Polypropylene (PP) Polystyrene (PS) Styrene butadiene (SBR) Acrylic-formaldehude (AF) | Lubricants Additives Catalysts Marine fuel oil Petroleum refining | Adhesives and sealants Agrochemicals Construction chemicals Corrosion control chemicals Cosmetics raw materials Electronic chemicals and materials Flavourings, fragrances, food additives Pharmaceutical drugs Specialty and industrial chemicals Specialty and industrial gases Inks, dyes and printing supplies Packaging, bottles, and containers Paint, coatings, and resins Polymer additives Specialty and life sciences chemicals Surfactants and cleaning agents |
See also
- Petroleum
- Petroleum products
- Instrumentation in petrochemical industries
- Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries
Asia Petrochemical Industry Conference(APIC)
Northeast of England Process Industry Cluster(NEPIC)
References
^ ab Sami Matar and Lewis F. Hatch (2001). Chemistry of Petrochemical Processes. Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 0-88415-315-0..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ ab Staff (March 2001). "Petrochemical Processes 2001". Hydrocarbon Processing: 71–246. ISSN 0887-0284.
^ Hassan E. Alfadala, G.V. Rex Reklaitis and Mahmoud M. El-Halwagi (Editors) (2009). Proceedings of the 1st Annual Gas Processing Symposium, Volume 1: January, 2009 – Qatar (1st ed.). Elsevier Science. pp. 402–414. ISBN 0-444-53292-7.CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Steam Cracking: Ethylene Production (PDF page 3 of 12 pages)
^ SBS Polymer Supply Outlook
^ Jean-Pierre Favennec (Editor) (2001). Petroleum Refining: Refinery Operation and Management. Editions Technip. ISBN 2-7108-0801-3.CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ "Timeline – Petrochemicals Europe". www.petrochemistry.eu. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
External links
![]() Media related to Petrochemicals at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Petrochemicals at Wikimedia Commons
