Transport network
| Network science | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| ||||
Network types | ||||
| ||||
Graphs | ||||
| ||||
| ||||
| ||||
Models | ||||
| ||||
| ||||
| ||||
A transport network, or transportation network is a realisation of a spatial network, describing a structure which permits either vehicular movement or flow of some commodity.[1][2]
Examples include but are not limited to road networks, railways, air routes, pipelines, aqueducts, and power lines.
Methods
Transport network analysis is used to determine the flow of vehicles (or people) through a transport network, typically using mathematical graph theory. It may combine different modes of transport, for example, walking and car, to model multi-modal journeys. Transport network analysis falls within the field of transport engineering. Traffic has been studied extensively using statistical physics methods.[3][4][5]
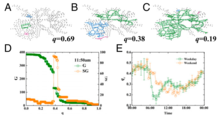
Fig. 1: Percolation traffic networks.
Recently a real transport network of Beijing was studied using network approach and percolation theory.[6] The research showed that one can characterize the quality of traffic in a city at each time in the day using percolation threshold, see Fig. 1.
See also
- Braess' paradox
- Flow network
- Heuristic routing
- Interplanetary Transport Network
- Network science
- Percolation theory
References
^ Barthelemy, Marc (2010). "Spatial Networks". Physics Reports. 499 (1–3): 1–101. arXiv:1010.0302. Bibcode:2011PhR...499....1B. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2010.11.002..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Boeing, G. (2017). "OSMnx: New Methods for Acquiring, Constructing, Analyzing, and Visualizing Complex Street Networks". Computers, Environment and Urban Systems. 65: 126–139. arXiv:1611.01890. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2017.05.004. Retrieved 2017-08-26.
^ Helbing, D (2001). "Traffic and related self-driven many-particle systems". Reviews of Modern Physics. 73 (4): 1067–1141. arXiv:cond-mat/0012229. Bibcode:2001RvMP...73.1067H. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.73.1067.
^ S., Kerner, Boris (2004). The Physics of Traffic : Empirical Freeway Pattern Features, Engineering Applications, and Theory. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. ISBN 9783540409861. OCLC 840291446.
^ Wolf, D E; Schreckenberg, M; Bachem, A (June 1996). Traffic and Granular Flow. Traffic and Granular Flow. WORLD SCIENTIFIC. p. 1. doi:10.1142/9789814531276. ISBN 9789810226350.
^ Li, Daqing; Fu, Bowen; Wang, Yunpeng; Lu, Guangquan; Berezin, Yehiel; Stanley, H. Eugene; Havlin, Shlomo (2015-01-20). "Percolation transition in dynamical traffic network with evolving critical bottlenecks". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (3): 669–672. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112..669L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1419185112. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4311803. PMID 25552558.
This article about transport is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
