Nordic Bronze Age
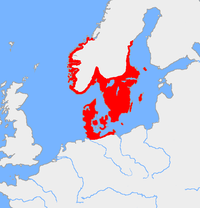
Map of the Nordic Bronze Age culture, c. 1200 BC
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 1700–500 BC. The Bronze Age culture of this era succeeded the Nordic Stone Age culture (Late Neolithic) and was followed by the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The archaeological legacy of the Nordic Bronze Age culture is rich, but the ethnic and linguistic affinities of it are unknown, in the absence of written sources. Some scholars also include sites in what is now Finland, Estonia, northern Germany and Pomerania, as part of its cultural sphere.
Contents
1 General characteristics
2 Sub-periodization
3 Climate
4 Religion and cult
5 Culture
6 See also
7 Notes
8 Bibliography
General characteristics
 |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Scandinavia |
|---|
Contemporary countries |
|
History |
|
Geography |
|
Other topics |
|
Settlement in the Scandinavian Bronze Age period consisted mainly of single farmsteads, with no towns or substantial villages known - farmsteads usually consisted of a longhouse plus additional four-post built structures (helms) - longhouses were initially two aisled, and after c.1300 BCE three aisled structure became normal. Evidence of multiple longhouses at a single site have been found, but they are thought to date to different periods, rather than being of the same date. Settlements were geographically located on higher ground, and tended to be concentrated near the sea. Also associated with settlements were burial mounds and cemeteries, with interments including oak coffins and urn burials; other settlement associations include rock carvings, or bronze hoards in wetland sites.[1]
Both agriculture (including wheat, millet, and barley) and keeping of domesticated animals (cattle, as well as sheep and pigs) were practiced, and fishing and shellfish were also sources of food, as well as deer, elk, and other wild animal hunting. There is evidence that oxen were used as draught animals, domesticated dogs were common, horses were rarer and probably status symbols.[1]
Even though Scandinavians joined the European Bronze Age cultures fairly late through trade, Scandinavian sites present a rich and well-preserved legacy of bronze and gold objects. These valuable metals were all imported, primarily from Central Europe, but they were often crafted locally and the craftsmanship and metallurgy of the Nordic Bronze Age was of a high standard. The archaeological legacy also comprise locally of crafted wool and wooden objects and there are many tumuli and rock carving sites from this period, but no written language existed in the Nordic countries during the Bronze Age. The rock carvings have been dated through comparison with depicted artifacts, for example bronze axes and swords. There are also numerous Nordic Stone Age rock carvings, those of northern Scandinavia mostly portray elk.
Thousands of rock carvings from this period depict ships, and the large stone burial monuments known as stone ships, suggest that ships and seafaring played an important role in the culture at large. The depicted ships, most likely represents sewn plank built canoes used for warfare, fishing and trade. These ship types may have their origin as far back as the neolithic period and they continue into the Pre-Roman Iron Age, as exemplified by the Hjortspring boat.[2] 3,600-year old bronze axes and other tools made from Cypriot copper have been found in the region.[3]
Sub-periodization
Oscar Montelius, who coined the term used for the period, divided it into six distinct sub-periods in his piece Om tidsbestämning inom bronsåldern med särskilt avseende på Skandinavien ("On Bronze Age dating with particular focus on Scandinavia") published in 1885, which is still in wide use. His absolute chronology has held up well against radiocarbon dating, with the exception that the period's start is closer to 1700 BC than 1800 BC, as Montelius suggested. For Central Europe a different system developed by Paul Reinecke is commonly used, as each area has its own artifact types and archaeological periods.

A broader subdivision is the Early Bronze Age, between 1700 BC and 1100 BC, and the Late Bronze Age, 1100 BC to 550 BC. These divisions and periods are followed by the Pre-Roman Iron Age.
Climate
The Nordic Bronze Age was initially characterized by a warm climate that began with a climate change around 2700 BC. The climate was comparable to that of present-day central Germany and northern France and permitted a relatively dense population and good opportunities for farming; for example, grapes were grown in Scandinavia at this time. A minor change in climate occurred between 850 BC and 760 BC, introducing a wetter, colder climate and a more radical climate change began around 650 BC.[4]
Religion and cult
There is no coherent knowledge about the Nordic Bronze Age religion; its pantheon, world view and how it was practised. Written sources are lacking, but archaeological finds draw a vague and fragmented picture of the religious practices and the nature of the religion of this period. Only some possible sects and only certain possible tribes are known. Some of the best clues come from tumuli, elaborate artifacts, votive offerings and rock carvings scattered across Northern Europe.
Many finds indicate a strong sun-worshipping cult in the Nordic Bronze Age and various animals have been associated with the sun's movement across the sky, including horses, birds, snakes and marine creatures (see also Sól). A female or mother goddess is also believed to have been widely worshipped (see Nerthus).[citation needed][clarification needed]Hieros gamos rites may have been common and there have been several finds of fertility symbols. A pair of twin gods are believed to have been worshipped, and is reflected in a duality in all things sacred: where sacrificial artifacts have been buried they are often found in pairs. Sacrifices (animals, weapons, jewellery and humans) often had a strong connection to bodies of water. Boglands, ponds, streams or lakes were often used as ceremonial and holy places for sacrifices and many artifacts have been found in such locations. Ritual instruments such as bronze lurs have been uncovered, especially in the region of Denmark and western Sweden. Lur horns are also depicted in several rock carvings and are believed to have been used in ceremonies.
Remnants of the Bronze Age religion and mythology are believed to exist in Germanic mythology and Norse mythology; e.g., Skinfaxi and Hrímfaxi and Nerthus, and it is believed to itself be descended from an older Indo-European proto-religion.
.mw-parser-output .mod-gallerydisplay:table.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-defaultbackground:transparent;margin-top:0.5em.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-centermargin-left:auto;margin-right:auto.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-leftfloat:left.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-rightfloat:right.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-nonefloat:none.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-collapsiblewidth:100%.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .titledisplay:table-row.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .title>divdisplay:table-cell;text-align:center;font-weight:bold.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .maindisplay:table-row.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .main>divdisplay:table-cell.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .captiondisplay:table-row;vertical-align:top.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .caption>divdisplay:table-cell;display:block;font-size:94%;padding:0.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .footerdisplay:table-row.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .footer>divdisplay:table-cell;text-align:right;font-size:80%;line-height:1em.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .gallerybox .thumb imgbackground:none.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .bordered-images imgborder:solid #eee 1px.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .whitebg imgbackground:#fff!important.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .gallerybox divbackground:#fff!important

Boat and sun symbols. Madsesbakke at Bornholm, Denmark.

Men with weapons. Tanumshede, western Sweden.

Sun wagon. Petroglyph depiction from Tanum, Sweden.

Sun cult artifacts. The Trundholm sun chariot, Denmark.

Ritualistic lur horns in bronze. Brudevælte, Denmark.

Ceremonial helmets. Veksø, Denmark.

Burial mounds. Gårdstånga, Skåne, Sweden.

Mound burials with oak coffins. Borum Eshøj Man, in Borum, Denmark.

Stone ship monuments. Gotland in Sweden.
Culture

Hunting scenes. Reindeer, hunters and fishing boats. Alta in Norway.

Agriculture. Ploughing with bulls. Petroglyph depiction from Tanum, Sweden.

Boats and sun symbols. Bardal Rock carvings, Steinkjer, Norway.

Metallurgy and tool making. Bronze saw mold, Sweden.

Wool clothing. Trindhøj man, Denmark.

Bronze combs. Gotland, Sweden.

Bronze razor knife for shaving. Scania, Sweden.

Bronze swords. Rørby, Denmark.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nordic Bronze Age. |
- Bronze Age Europe
- Bronze Age sword
- Egtved Girl
- The King's Grave
- Stone ships
- Tanumshede
- Pomeranian culture
Notes
^ ab Thrane, Henrik, Peregrine, Peter N.; Ember, Melvin, eds., "Scandinavian Bronze Age", Encyclopedia of Prehistory, 4 (Europe), pp. 299–314.mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Ling 2008. Elevated Rock Art. GOTARC Serie B. Gothenburg Archaeological Thesis 49. Department of Archaeology and Ancient History, University of Gothenburg, Goumlteborg, 2008.
ISBN 978-91-85245-34-5.
^ https://www.realmofhistory.com/2016/05/17/cypriot-copper-axes-bronze-age-sweden/
^ Kane, Njord (1 November 2016). The Viking Stone Age: Birth of the Ax Culture. Spangenhelm Publishing.|access-date=requires|url=(help)
Bibliography
- Dabrowski, J. (1989) Nordische Kreis un Kulturen Polnischer Gebiete. Die Bronzezeit im Ostseegebiet. Ein Rapport der Kgl. Schwedischen Akademie der Literatur Geschichte und Alter unt Altertumsforschung über das Julita-Symposium 1986. Ed Ambrosiani, B. Kungl. Vitterhets Historie och Antikvitets Akademien. Konferenser 22. Stockholm.
- Davidson, H. R. Ellis and Gelling, Peter: The Chariot of the Sun and other Rites and Symbols of the Northern European Bronze Age.
- K. Demakopoulou (ed.), Gods and Heroes of the European Bronze Age, published on the occasion of the exhibition "Gods and Heroes of the Bronze Age. Europe at the Time of Ulysses", from December 19, 1998, to April 5, 1999, at the National Museum of Denmark, Copenhagen, London (1999),
ISBN 0-500-01915-0. - Demougeot, E. La formation de l'Europe et les invasions barbares, Paris: Editions Montaigne, 1969-1974.
- Kaliff, Anders. 2001. Gothic Connections. Contacts between eastern Scandinavia and the southern Baltic coast 1000 BC – 500 AD.
Montelius, Oscar, 1885. Om tidsbestämning inom bronsåldern med särskilt avseende på Skandinavien.- Musset, L. Les invasions: les vagues germanique, Paris: Presses universitaires de France, 1965.
















