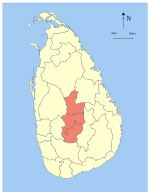
Central Province, Sri Lanka
Central Province මධ්යම පළාත மத்திய மாகாணம் | ||
|---|---|---|
Province | ||
 Kandy | ||
| ||
 Location within Sri Lanka | ||
| Coordinates: 7°20′N 80°45′E / 7.333°N 80.750°E / 7.333; 80.750Coordinates: 7°20′N 80°45′E / 7.333°N 80.750°E / 7.333; 80.750 | ||
| Country | Sri Lanka | |
| Created | 1833 | |
| Admitted | 14 November 1987 | |
| Capital | Kandy | |
| Largest City | Kandy | |
| Government | ||
| • Governor | P. B. Dissanayake | |
| • Chief Minister | Sarath Ekanayake | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 5,674 km2 (2,191 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 6th (8.63% of total area) | |
| Population (2011 census) | ||
| • Total | 2,558,716 | |
| • Rank | 2nd (12.97% of total pop.) | |
| • Density | 450/km2 (1,200/sq mi) | |
Gross Regional Product (2010)[1] | ||
| • Total | Rs 465 billion | |
| • Rank | 4th (9.6% of total) | |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (Sri Lanka) | |
| ISO 3166 code | LK-2 | |
| Vehicle registration | CP | |
| Official languages | Sinhalese, Tamil | |
| Website | www.cp.gov.lk | |
The Central Province (Sinhalese: මධ්යම පළාත Madhyama Palata, Tamil: மத்திய மாகாணம் Madhiya Maakaanam) is one of the nine provinces of Sri Lanka, the first level administrative division of the country. (The provinces have existed since the 19th century but did not have any legal status until 1987 when the 13th Amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka established provincial councils.[2][3]) The Central Province is primarily in the central mountainous terrain of Sri Lanka. It is the 6th largest province by area and is home to 2.5 million people. It is bordered by North Central Province to the north, Uva Province to the east, North Western Province to the west and Sabaragamuwa Province to the south and west. The province's capital is Kandy.
The cities of Matale and Nuwara Eliya are in the Central Province. The province is famous for its production of Ceylon tea, planted by the British in the 1860s after a devastating disease killed all the coffee plantations in the province. The Central Province attracts many tourists, with hill station towns such as Gampola, Hatton and Nuwara Eliya.
Contents
1 History
2 Geography
2.1 Mountain ranges
2.2 Climate
3 Demographics
3.1 Ethnicity
4 Administrative divisions
4.1 Districts
4.2 Divisional secretariats
4.3 Major cities
5 See also
6 References
7 Maps
8 External links
History
Though three successive European powers invaded Sri Lanka during the 16th to the 19th century, the Central Province maintained its independence until the early 19th century when the British conquered Kandy. The British then established a colonial headman ranking system in 1824, which came into effect in 1832.
- Colonial head mudaliyars
- Sir Christofel de-Silva (1824–1842)
- Don William Gunawardene De-Saram III (1842–1856)
- Sir Hendrick Ekanayake (1856–1860)
- Sir Alexander-James Divakara Mohotti (1860–1888)
- Don Agaris Divakara Mohotti (1888–1924)
The Mudaliyar Office was abolished in 1924 and the last of the colonial headman retired from their positions and gave up the rule to the British officers in 1926. All headman positions were then passed down to the newly elected governor-general of Central Province. This was established in 1929 as a way for the British to directly rule the provinces.
The historic Matale city, Temple of the Tooth, Dambulla cave temple, Aluwihare temple and the Sigiriya rock are in the Central Province.
Geography
The province has an area of 5,674 km² and a population of 2,421,148. Major towns include Kandy (119,186), Matale (39,869), Dambulla (75,290), Gampola (26,481), Nuwara Eliya (27,449) and Hatton (16,790).
Mountain ranges
Knuckles Mountain Range, Adam's Peak and Horton Plains are UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the Central Province.
Climate
The climate is cool, and many areas above 1,500 metres often have chilly nights. The western slopes are very wet, some places have almost 7,000 mm of rain per year. The eastern slopes are parts of the mid-dry zone as it is receiving rain only from North-Eastern monsoon. The temperatures range from 24°C at Kandy to just 16°C in Nuwara Eliya, which is 1,889 m above sea level. The highest mountains in Sri Lanka are in the Central Province. The terrain is mostly mountainous, with deep valleys cutting into it. The two main mountain regions are the central massif and the Knuckles range to the east of Kandy.
Demographics
The population is a mixture of Sinhalese, Tamil and the Moors. Many tea plantation workers are Indian Tamils, brought over to Sri Lanka by the British in the 19th century.
Ethnicity
| Ethnic group | Population | % |
|---|---|---|
Sinhala | 1,584,100 | 65.35% |
Indian Tamil | 482,945 | 19.92% |
Sri Lankan Moor | 223,076 | 9.2% |
Sri Lankan Tamil | 122,438 | 5.05% |
| Burger | 3,589 | 0.15% |
| other | 7,818 | 0.32% |
Total | 2,423,966 | 100.00% |
Administrative divisions
Central Province is divided into three districts and 36 divisional secretariats.
Districts
district | Capital | Area (km²) | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
Kandy District | Kandy | 1,940 | 1,279,028 |
Matale District | Matale | 1,993 | 441,328 |
Nuwara Eliya District | Nuwara Eliya | 1,741 | 703,610 |
Divisional secretariats
The districts of the Sri Lanka are divided into administrative sub-units known as divisional secretariats. These were originally based on the feudal counties, the korales and ratas. They were formerly known as 'D.R.O. Divisions' after the 'Divisional Revenue Officer'. Later the D.R.O.s became 'Assistant Government Agents' and the Divisions were known as 'A.G.A. Divisions'. Currently, the divisions are administered by a 'Divisional Secretary' and are known as a 'D.S. Divisions'.
There are 36 divisional secretariats in Central Province, which are listed below, by district. There are 20 in Kandy District, 11 in Matale District and 5 in Nuwara Eliya District.
Major cities
Rank | City | Admin. District | Pop. | Rank | City | Admin. District | Pop. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kandy | Kandy | 119,186 | 7 | Nawalapitiya | Kandy | 14,685 |
| 2 | Dambulla | Matale | 75,290 | 8 | Talawakele | Nuwara Eliya | 3,458 |
| 3 | Matale | Matale | 39,869 | 9 | Harispattuwa | Kandy | 1,690 |
| 4 | Nuwara Eliya | Nuwara Eliya | 27,449 | 10 | Kadugannawa | Kandy | 1,323 |
| 5 | Gampola | Kandy | 26,481 | 11 | Sigiriya | Matale | 1,068 |
| 6 | Hatton | Kandy | 16,790 | ||||
| 2009 estimate[4] | |||||||
See also
- Provinces of Sri Lanka
- Districts of Sri Lanka
- Tea production in Sri Lanka
References
^ :.News Line : North, East record highest GDP growth rate Archived 2012-06-20 at the Wayback Machine
^ "Provinces of Sri Lanka". Statoids..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Provincial Councils". Government of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 2009-07-07.
^ "World Gazetteer: Sri Lanka - largest cities (per geographical entity)". archive.ph. 16 December 2012. Archived from the original on 16 December 2012.
Maps
- Searchable Map of Sri Lanka
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Central Province, Sri Lanka. |
- Central Provincial Council Sri Lanka
- Office of the Council Secretary – Central Provincial Council Sri Lanka
- Cheief Secretary's Office – Central Provincial Council Sri Lanka
- Central Provincial Postal Codes Sri Lanka
- Cities in Central province