Central European Summer Time
[dummy-text]
Central European Summer Time
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
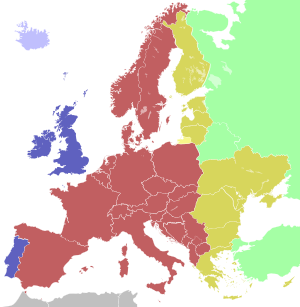
Time in Europe:
| light blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time (UTC+1) | |
| red | Central European Time (UTC+1) |
Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) | |
| yellow | Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time (UTC+2) |
| golden | Eastern European Time (UTC+2) |
Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) | |
| light green | Further-eastern European Time / Moscow Time / Turkey Time (UTC+3) |
Central European Summer Time (CEST), sometime referred also as Central European Daylight Time (CEDT), is the standard clock time observed during the period of summer daylight-saving in those European countries which observe Central European Time (UTC+1) during the other part of the year. It corresponds to UTC+2, which makes it the same as Central Africa Time, South African Standard Time and Kaliningrad Time in Russia.[1]
Contents
1 Names
2 Period of observation
3 Usage
4 See also
5 References
Names[edit]
Other names which have been applied to Central European Summer Time are Middle European Summer Time (MEST)[2], Central European Daylight Saving Time (CEDT)[3], and Bravo Time (after the second letter of the NATO phonetic alphabet)[4]. It is also in practice called CET, for example in invitations to events during the summer.
Period of observation[edit]
Since 1996 European Summer Time has been observed between 1:00 UTC (2:00 CET and 3:00 CEST) on the last Sunday of March and 1:00 UTC on the last Sunday of October; previously the rules were not uniform across the European Union.[5]
Usage[edit]
The following countries and territories use Central European Summer Time.[6]
Albania, regularly since 1974
Andorra, regularly since 1985
Austria, regularly since 1980
Belgium, regularly since 1980
Bosnia and Herzegovina, regularly since 1983
Croatia, regularly since 1983
Czech Republic, regularly since 1979
Denmark (metropolitan), regularly since 1980
France (metropolitan), regularly since 1976
Germany, regularly since 1980
Gibraltar, regularly since 1982
Hungary, regularly since 1983
Italy, regularly since 1968
Kosovo, regularly since 1983
Liechtenstein regularly since 1981
Luxembourg, regularly since 1981
Malta, regularly since 1974
Monaco, regularly since 1976
Montenegro, regularly since 1983
Netherlands, regularly since 1977
Norway, regularly since 1980
Poland, regularly since 1977
Republic of Macedonia, regularly since 1983
San Marino, regularly since 1966
Serbia, regularly since 1983
Slovakia regularly since 1979
Slovenia, regularly since 1983
Spain (except Canary Islands, which apply Western European Summer Time instead), regularly since 1974
Sweden, regularly since 1980
Switzerland, regularly since 1981
Vatican, regularly since 1966
CEST was used also in the years 1993–1995 in Portugal, 1998–1999 in Lithuania and 2005–2008 in Tunisia. In addition, Libya used CEST during the years 1951–1959, 1982–1989, 1996–1997 and 2012–2013.
See also[edit]
- European Summer Time
- Other countries and territories in UTC+2 time zone
- Other names of UTC+2 time zone
References[edit]
^ "CEST time now". 24timezones.com. Retrieved 2018-07-20..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Time zone names- Middle European Daylight, Middle European Summer, Mitteieuropaische Sommerzeit (german)". www.worldtimezone.com. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
^ "CEDT - Central European Daylight Time: Current local time". Time Difference. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
^ "B – Bravo Time Zone (Time Zone Abbreviation)". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
^ Joseph Myers (2009-07-17). "History of legal time in Britain". Retrieved 2009-10-11.
^ "CEST – Central European Summer Time (Time Zone Abbreviation)". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2018-07-20.
Categories:
- Time zones
- Daylight saving time
- Time in Europe
- Geography of Central Europe
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"0.152","walltime":"0.191","ppvisitednodes":"value":371,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":10424,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":281,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":7,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":0,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":1,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":15062,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":0,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 152.502 1 -total"," 93.27% 142.231 1 Template:Reflist"," 79.00% 120.471 6 Template:Cite_web"," 3.56% 5.429 1 Template:Time_zones_of_Europe"," 2.44% 3.727 1 Template:Main_other"," 1.36% 2.070 7 Template:Nowrap"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.080","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":2463558,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw1246","timestamp":"20181123182931","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false);mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":94,"wgHostname":"mw1319"););

