Krishna River
| Krishna | |
 Krishna river gorge by Srisailam, Andhra Pradesh, India | |
| Country | India |
|---|---|
| States | Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh |
| Region | Southern Peninsular India |
Tributaries | |
| - left | Bhima, Dindi, Peddavagu, Musi, Paleru, Munneru |
| - right | Venna, Koyna, Panchganga, Dudhaganga, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, Tungabhadra |
| Source | Near Mahabaleswar, Jor village |
| - location | Satara district, Maharashtra, India |
| - elevation | 914 m (2,999 ft) Geographic headwaters |
| - coordinates | 17°59′18.8″N 73°38′16.7″E / 17.988556°N 73.637972°E / 17.988556; 73.637972 |
| Mouth | Hamsaladeevi, Krishna district, Andhra Pradesh |
| - location | Bay Of Bengal, India |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 15°44′10.8″N 80°55′12.1″E / 15.736333°N 80.920028°E / 15.736333; 80.920028Coordinates: 15°44′10.8″N 80°55′12.1″E / 15.736333°N 80.920028°E / 15.736333; 80.920028 [1] |
| Length | 1,300 km (808 mi) approx. |
| Basin | 258,948 km2 (99,980 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 2,213 m3/s (78,151 cu ft/s) [2] |
Discharge elsewhere (average) | |
| - Vijayawada (1901–1979 average), max (2009), min (1997) | 1,641.74 m3/s (57,978 cu ft/s) |
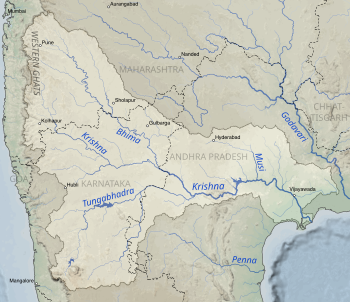 Drainage basin of the Krishna in the South Indian Peninsula | |

Down stream view of Prakasam Barrage.

Krishna river near Vijayawada
The Krishna River is the fourth-biggest river in terms of water inflows and river basin area in India, after the Ganga, Godavari and Brahmaputra. The river is almost 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) long. The river is also called Krishnaveni. It is a major source of irrigation for Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.[3]
Contents
1 Sources
2 Tributaries
3 Krishna Basin
4 Places and temples
5 Flora and fauna
6 Waterfalls
7 Bridges
8 Floods
9 Interstate water sharing
10 Dams
11 Hydroelectric power stations
12 Mineral deposits
13 Pollution
14 See also
15 References
Sources
The Krishna river originates in the Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar at an elevation of about 1,300 metres, in the state of Maharashtra in central India. It is one of the longest rivers in India. The Krishna river is around 1,300 km in length.
The Krishna river's source is at Mahabaleswar near the Jor village in the extreme north of Wai Taluka, Satara District, Maharashtra in the west and empties into the Bay of Bengal at Hamasaladeevi (near Koduru) in Andhra Pradesh, on the east coast. It flows through the state of Karnataka before entering Telangana State. The delta of this river is one of the most fertile regions in India and was the home to ancient Satavahana and Ikshvaku Sun Dynasty kings. Vijayawada is the largest city on the River Krishna.
It causes heavy soil erosion during the monsoon floods. It flows fast and furious, often reaching depths of over 75 feet (23 m). Ironically, there is a saying in Marathi: "Shant vaahate Krishnamaai" which means "quiet flows Krishna". This term is used to describe that a person should be as quiet as Krishna.
Tributaries

Panoramic view of Ujjani or Bhima Dam

Tungabhadra Dam near Hosapete
| Right-bank tributary | Town, District, State of confluence | Left-Bank Tributary |
|---|---|---|
| Venna River | Sangam Mauli, Satara, Maharashtra | |
| Urmodi river | Kashil, Satara, Maharashtra | |
| Tarali/Kali Ganga river | Umbraj, Satara, Maharashtra | |
| Mand river | Umbraj, Satara, Maharashtra | |
| Tasawade, Satara, Maharashtra | Kolamba river | |
| Koyna River | Karad, Satara, Maharashtra | |
| Bramhanal, Sangli, Maharashtra | Yerla river | |
| Warna River | Haripur, Sangli, Maharashtra | |
| Panchganga River | Narsobawadi, Sangli, Mahrashtra | |
| Dudhaganga | Yadur, Belgaum, Karnataka | |
| Hippagiri barrage | ||
| Ghataprabha River | Almatti, Bagalkot District, Karanataka | |
| Almatti Dam | ||
| Malaprabha River | Kudala Sangam, Bagalkot District, Karanataka | |
| Basava Sagar Reservoir | ||
| Ammapur, Kalburgi, Karnataka | Doni River | |
| Kadlur, Raichur, Karnataka | Bhima River | |
| Jurala dam | ||
| Lower Jurala dam | ||
| Tungabhadra River | Alampur, Mahaboobnagar, Telangana | |
Srisailam temple | Srisailam Dam | |
| Srisailam tail pond weir | ||
| Nalgonda district, Telangana | Dindi River | |
Nagarjuna Sagar dam | ||
| Chityala, Nalgonda | Haliya River | |
Nagarjuna Sagar tail pond dam | ||
| Wazirabad, Nalgonda, Telangana | Musi River | |
Pulichintala dam, Suryapet district | ||
| Mukteswarapuram, Krishna district | Paleru River | |
| Amaravathi village, Guntur district | Munneru River | |
| Ibrahimpatnam, Krishna district | Polavaram right bank canal | |
| Kondaveeti vagu[4] | Ibrahimpatnam, Krishna district | Budameru diversion channel |
Amaravati city | Prakasam Barrage | Vijayawada city |
| National Waterway 4 | Prakasam Barrage | National Waterway 4 |
The largest tributary of the Krishna River is the Tungabhadra River with a drainage basin measuring 71,417 km2 (27,574 sq mi), running for about 531 km (330 mi), but the longest tributary is the Bhima River, which makes a total run of 861 km (535 mi) and has an equally large drainage area of 70,614 km2 (27,264 sq mi).
Three tributaries Panchganga, Warna and Yerla meet Krishna river near Sangli. These places are considered very holy. It is said that Lord Dattatreya spent some of his days at Audumber on the banks of river Krishna.
Sangameswaram of Kurnool district in Andhra Pradesh is a famous pilgrim center for Hindus where Tungabhadra and Bhavanasi rivers join the Krishna river. The Sangameswaram temple is now drowned in the Srisailam reservoir, and visible for devotees only during summer when the reservoir's water level comes down.[5]
Krishna Basin
Drainage Basin of Krishna
Bhima Upper (17.58%)
Bhima Lower (9.29%)
Krishna Upper (21.39%)
Krishna Middle (8.73%)
Krishna Lower (15.50%)
Tungabhadra Upper (11.20%)
Tungabhadra Lower (16.31%)
Krishna Basin extends over an area of 258,948 km2 (99,980 sq mi) which is nearly 8% of the total geographical area of the country. This large basin lies in the states of Karnataka (113,271 km2), Telangana, Andhra Pradesh (76,252 km2) and Maharashtra (69,425 km2).[6]
The Krishna river rises in the Western Ghats, at an elevation of about 1,337 m (4,386 ft) just north of Mahabaleshwar, about 64 km (40 mi) from the Arabian Sea. It flows for about 1,400 km (870 mi) and outfalls into the Bay of Bengal. The principal tributaries joining Krishna are the Ghataprabha River, Malaprabha River, Bhima River, Tungabhadra River and Musi River.
Most of this basin comprises rolling and undulating country, except for the western border, which is formed by an unbroken line of the Western Ghats. The important soil types found in the basin are black soils, red soils, laterite and lateritic soils, alluvium, mixed soils, red and black soils and saline and alkaline soils.
An average annual surface water potential of 78.1 km3 has been assessed in this basin. Out of this, 58.0 km3 is utilizable water.[7] Culturable area in the basin is about 203,000 km2 (78,000 sq mi), which is 10.4% of the total cultivable area of the country. As the water availability in the Krishna river was becoming inadequate to meet the water demand, Godavari River is linked to the Krishna river by commissioning the Polavaram right bank canal with the help of Pattiseema lift scheme in the year 2015 to augment water availability to the Prakasam Barrage in Andhra Pradesh.[8] The irrigation canals of Prakasam Barrage form part of National Waterway 4.
Agumbe which receives second highest rainfall (7,620 mm mean annual) in India, is located in the Krishna river basin. Mullayanagiri peak in Karnataka at an altitude of 1,930 m (6,330 ft) above msl, is the highest point of the Krishna basin.
Places and temples

Pre Historic sites of Middle Krishna-tungabhadra Valley in Telangana, Andhra Pradesh
this river is revered by Hindus as sacred. The river is also believed to remove all sins of people by taking a bath in this river. The centre of attraction is the Krishna Pushkaram fair which is held once in twelve years on the banks of the Krishna river. There are many pilgrimage places in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh on the course of the river.[citation needed]
The first holy place on the river Krishna is at Wai, known for the Mahaganpati Mandir and Kashivishweshwar temple. It has seven ghats along the river.Temples like Dattadeva temple, which is revered by the people of Maharashtra, are located on the banks of Krishna at Narsobawadi and Audumbar near Sangli. Also, located on the banks of the river Krishna are the Sangameshwar Shiva temple at Haripur, goddess Durga temple in Vijayawada and Ramling temple near Sangli, Mallikarjuna Jyotirlinga (Srisailam), Amareshwara Swamy temple (Amaravati (state capital)), Dattadeva temple, Sangameshwara Shiva temples at Alampur in Telangana.[citation needed]
Flora and fauna
Wide spread area near to the Krishna river holds the rich flora and fauna. The last surviving Mangrove forests in the Krishna estuary have been declared as the Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary. The sanctuary is the home to the large number of resident and migratory birds. Fishing cat, otter, Estuarine crocodile, spotted deer, sambar, black buck, snake, lizards and jackal can also be spotted in the sanctuary. The sanctuary also supports rich vegetation with plants like Rhizophora, Avicennia, and Aegiceros. The following are few other wildlife sanctuaries located in the river basin.
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve
- Rollapadu Wildlife Sanctuary
- Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary
- Ghataprabha Bird Sanctuary
- Gudavi Bird Sanctuary
- Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary
- Radhanagari Wildlife Sanctuary
- Great Indian Bustard Sanctuary
- Chandoli National Park
- Kudremukh National Park
- Kasu Brahmananda Reddy National Park
- Mahavir Harina Vanasthali National Park
- Mrugavani National Park
- Pakhal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Ranibennur Blackbuck Sanctuary
- Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary
- Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary, Bellary
Waterfalls

Gokak Falls on Ghataprabha river
The following are few other waterfalls located in the river basin
Ethipothala on Chandravanka river which is the tributary of river Krishna river
Godchinamalaki on Markandeya river a tributary of Ghataprabha
Gokak on Ghataprabha- Mallela Theertham
Bridges

Panorama of Prakasam Barrage and Railway bridges on Krishna near Vijayawada
The Krishna River is spanned by several bridges along its course, some of which are listed below.
- Krishna Bridge, Wai, Maharashtra – This bridge, which is located in the Dharmpuri Peth area of the town of Wai, is one of the oldest bridges that were built by the British in India. It spans the Krishna over nine kamans (arches) and is made of black rock. The bridge serves as a flood mark (when the water rises to the level of the road on the bridge) for the "Waikar" people.
- Irwin Bridge, Sangli – This is one of the oldest, historic and largest bridges over the Krishna that were built by the British. The Irwin Bridge, which is built of reddish stone, has two passages where one can climb down to the river in the middle of its span to view the water.
- Kudachi - Ugar Railway bridge built by the British in 1891.
- B. Soundatti Bridge, Raibag – This is also one of the oldest bridges built during the British rule. This bridge connects Maharashtra to Karnataka state.
- Tangadagi Bridge, This is one of oldest bridge that connects the Bijapur and Bagalkot Districts of Karnataka. God Neelambika Temple is there at the bank of Krishna River.
Floods
In October 2009, heavy floods occurred, isolating 350 villages and leaving millions homeless,[9] which is believed to be first occurrence in 1000 years. The flood resulted in heavy damage to Kurnool, Mahabubnagar, Guntur, Krishna and Nalagonda Districts. The entire city of Kurnool was immersed in approximately 10 ft (3 m) water for nearly 3 days.[10]
Water inflow of 1,110,000 cu ft/s (31,000 m3/s) was recorded at the Prakasam Barriage, which surpassed the previous record of 1,080,000 cu ft/s (31,000 m3/s) recorded in the year 1903.[11] Krishna river is the second largest east flowing river of the peninsula. The flood waters of Krishna and Godavari rivers can be fully utilized by exporting water to other east flowing peninsular rivers up to Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu by constructing a coastal reservoir on the Bay of Bengal sea area.[12]
Interstate water sharing
At present, the award of Bachawat tribunal dated 31 May 1976 is applicable for sharing the water available in the river among the riparian states. The Brijesh Kumar tribunal award given on 29 November 2013 is challenged by Andhra Pradesh in the Supreme Court and the case pending since then.[13] Newly created Telangana state also approached Supreme Court demanding a fresh tribunal hearing to secure its water needs on equitable basis.[14]
Dams

Nagarjuna Sagar Dam Gates view
There are many dams constructed across the Krishna river.[15]
- Dhom Dam
- Hippagiri barrage
- Almatti Dam
- Narayanpur Dam
- Bhima Dam
- Jurala Dam
- Srisailam Dam
- Nagarjuna Sagar Dam
- Nagarjuna Sagar tail pond
- Pulichinthala Dam
- Prakasam Barrage
- Tungabhadra Dam
- Rajolibanda barrage
- Sunkesula barrage
Hydroelectric power stations
Krishna river is one of the rivers whose water energy is harnessed to a large extent by various hydro electric power stations in India.[16] The following is the list of hydro electric power stations excluding small and medium installations.

Almatti Dam with its right bank power house
| Name of the project | Rated Power (in MW) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Koyna Hydroelectric Project | 1,920 | Power station with Pumped-storage hydroelectricity units |
| Mulshi Dam | 300 | Power station with Pumped-storage hydroelectricity units |
| Thokarwadi Dam | 72 | |
| Ujjani Dam | 12 | Power station with Pumped-storage hydroelectricity units |
| Almatti Dam | 290 | |
| Bhadra Dam | 39 | |
| Tungabhadra Dam | 127 | |
| Jurala Hydroelectric Project | 240 | |
| Lower Jurala Hydro Electric Project | 240 | |
| Srisailam Dam | 1,670 | Power station with Pumped-storage hydroelectricity units |
| Nagarjuna Sagar Dam | 960 | Power station with Pumped-storage hydroelectricity units |
| Nagarjuna Sagar tail pond | 50 | |
| Pulichinthala Dam | 120 |
Mineral deposits

Krishna close to its origin at Menawali, near Wai, Satara district, Maharashtra.18th century, Maratha statesman, Nana Fadnavis built the Ghat and a palace here.This location has been used in many Hindi movies.
Krishna river basin is endowed with rich mineral deposits such as oil & gas, coal, iron, lime stone, dolomite, gold, granite, laterite, uranium, diamonds, etc. The following are the few noted deposits:
Krishna Godavari Basin, oil & gas
Yellandu, coal
Bayyaram Mines, iron
Kudremukh, iron
Donimalai, iron- Jaggayapeta mines, dolomite
Nalgonda uranium deposits,
Kollur Mine, diamonds
Hatti Gold Mines,
Pollution

The Deccan Traps near Pune
Most of the years, the river water is not joining the sea due to full utilisation of water mainly in agriculture.[17][18] Closed river basin of Krishna means that the river ecosystem is on the verge of death.[19][20] The river receives the waste from the large number of cities and the river basin population has increased to 80 million enhancing pollution load many folds into the river. Adequate average and minimum continuous environmental flows to the sea are not taking place in most of the years constricting salt export and leading to formation of saline and sodic alkaline soils in the lower reaches of the river basin.[21][22]High alkalinity water is discharged from the ash dump areas of many coal fired power stations into the river which further increases the alkalinity of the river water whose water is naturally of high alkalinity since the river basin is draining vast area of basalt rock formations.[23] The following are the few coal fired power stations located in the river basin
| Name of Power Station | Rated Power (in MW) |
|---|---|
| Vijayawada Thermal Power Station | 1,760 |
| Raichur Thermal Power Station | 1,470 |
| Bellary Thermal Power station | 1,700 |
| Yermarus Thermal Power Station | 1,600 |
| Solapur Super Thermal Power Station | 1,320 |
| Kudgi Super Thermal Power Project | 2,400 |
| Yadadri Thermal Power Plant | 4000 |
See also
|
|
|
|
References
^ Krishna at GEOnet Names Server
^ Kumar, Rakesh; Singh, R.D.; Sharma, K.D. (2005-09-10). "Water Resources of India" (PDF). Current Science. Bangalore: Current Science Association. 89 (5): 794–811. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 April 2017. Retrieved 2013-10-13..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Map of Krishna River basin" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 August 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
^ "Lower Krishna basin watershed map" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 April 2017. Retrieved 21 March 2016.
^ Srisailam project manual
^ "Krishna basin status report, March 2014" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
^ IWMI Research Report 83. "Spatial variation in water supply and demand across river basins of India" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
^ "How the Krishna went dry?". Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
^
"Flooding along the Krishna River: Natural Hazards". earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 21 February 2017. Retrieved 11 October 2009.
^ "Agony of Floods: Flood Induced Water Conflicts in lndia [sic]" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
^ "Managing historic flood in the Krishna river basin in the year 2009". Archived from the original on 26 October 2017. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
^ "Feasibility of coastal reservoir to harness Godavari river surplus waters". Retrieved 21 September 2018.
^ Hindu daily dated. "Court: do not publish KWDT-II decision". Retrieved 5 November 2012.
^ "T-State wants tribunal to adjudicate water disputes". Retrieved 12 July 2014.
^ "Headworks (Dam, Barrage, Weir, Anicut, Lift)". Archived from the original on 21 September 2017. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
^ "Power Houses in Krishna Basin". Archived from the original on 18 August 2016. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
^ J. Keller, A. Keller and G. Davids. "River basin development phases and implications of closure" (PDF). Retrieved 25 August 2012.
^ "IWMI Research report nos # 1, 3, 14, 56, 72, 83, 107, 111, 121, 123, 125 etc". Archived from the original on 6 June 2017. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
^ "Technology Breakthroughs for Global water security" (PDF). Retrieved 20 October 2018.
^ "Do not kill a river". Archived from the original on 13 August 2017. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
^ Oregon State University, USA. "Managing irrigation water quality" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
^ "Alkalinity and salinity bane of soil in T state". Archived from the original on 2 January 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
^ Chemical weathering in the Krishna Basin and Western Ghats of the Deccan Traps, India
21. Refer 'theertha prabhanda'(sanskrit).