Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Motto(s): Latin: Multis e Gentibus Vires[1] ("Strength from Many Peoples") | |||
BC AB SK MB ON QC NB PE NS NL YT NT NU  | |||
| Confederation | September 1, 1905 (split from NWT) (8th/9th, simultaneously with Alberta) | ||
| Capital | Regina | ||
| Largest city | Saskatoon | ||
| Largest metro | Saskatoon metropolitan area | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Constitutional monarchy | ||
| • Lieutenant governor | W. Thomas Molloy | ||
| • Premier | Scott Moe (Saskatchewan Party) | ||
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan | ||
| Federal representation | (in Canadian Parliament) | ||
| House seats | 14 of 338 (4.1%) | ||
| Senate seats | 6 of 105 (5.7%) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 651,900 km2 (251,700 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 591,670 km2 (228,450 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 59,366 km2 (22,921 sq mi) 9.1% | ||
| Area rank | Ranked 7th | ||
| 6.5% of Canada | |||
| Population (2016) | |||
| • Total | 1,098,352 [2] | ||
| • Estimate (2018 Q4) | 1,165,903 [3] | ||
| • Rank | Ranked 6th | ||
| • Density | 1.86/km2 (4.8/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Saskatchewanian (official),[4]also Saskatchewanite | ||
| Official languages | English[5] | ||
GDP | |||
| • Rank | 5th | ||
| • Total (2015) | C$79.415 billion[6] | ||
| • Per capita | C$70,138 (4th) | ||
| Time zone | Central: UTC−6, year-round in most areas Mountain: UTC-7/-6, Lloydminster and nearby areas | ||
| Postal abbr. | SK | ||
| Postal code prefix | S | ||
| ISO 3166 code | CA-SK | ||
| Flower | Western red lily | ||
| Tree | Paper birch | ||
| Bird | Sharp-tailed grouse | ||
| Website | www.saskatchewan.ca | ||
| Rankings include all provinces and territories | |||
Saskatchewan (/səˈskætʃəwən, sæ-, -wɒn/ (![]() listen)) is a prairie and boreal province in western Canada, the only province without natural borders. It has an area of 651,900 square kilometres (251,700 sq mi), nearly 10 percent of which (59,366 square kilometres (22,900 sq mi)) is fresh water, composed mostly of rivers, reservoirs, and the province's 100,000 lakes.
listen)) is a prairie and boreal province in western Canada, the only province without natural borders. It has an area of 651,900 square kilometres (251,700 sq mi), nearly 10 percent of which (59,366 square kilometres (22,900 sq mi)) is fresh water, composed mostly of rivers, reservoirs, and the province's 100,000 lakes.
Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. As of late 2017, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,163,925.[7] Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern boreal half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Of the total population, roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon, or the provincial capital Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, and the border city Lloydminster (partially within Alberta).[8]
Saskatchewan is a landlocked province with large distances to moderating bodies of waters. As a result, its climate is extremely continental, rendering severe winters throughout the province. Southern areas have very warm or hot summers. Midale and Yellow Grass near the U.S. border are tied for the highest ever recorded temperatures in Canada with 45 °C (113 °F) observed at both locations on July 5, 1937.[9][10] In winter, temperatures below −45 °C (−49 °F) are possible even in the south during extreme cold snaps.
Saskatchewan has been inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous groups, and first explored by Europeans in 1690 and settled in 1774. It became a province in 1905, carved out from the vast North-West Territories, which had until then included most of the Canadian Prairies. In the early 20th century the province became known as a stronghold for Canadian social democracy; North America's first social-democratic government was elected in 1944. The province's economy is based on agriculture, mining, and energy. Saskatchewan's current lieutenant governor is Thomas Molloy and the current premier is Scott Moe.
In 1992, the federal and provincial governments signed a historic land claim agreement with First Nations in Saskatchewan.[11] The First Nations received compensation and were permitted to buy land on the open market for the bands; they have acquired about 3,079 square kilometres (761,000 acres; 1,189 sq mi), now reserve lands. Some First Nations have used their settlement to invest in urban areas, including Saskatoon.[11]
Contents
1 Etymology
2 Geography
2.1 Climate
3 History
3.1 European settlements
3.2 20th century
3.3 1914–39
3.4 Recent history
4 Demographics
4.1 Municipalities
5 Economy
5.1 Provincial finances
6 Government and politics
6.1 Law enforcement
7 Education
8 Healthcare
9 Transportation
10 Arts and culture
11 Sports
12 Provincial symbols
12.1 Centennial celebrations
13 Climate
14 See also
15 References
16 Further reading
17 External links
Etymology
Its name derived from the Saskatchewan River. The river was known as kisiskāciwani-sīpiy ("swift flowing river") in the Cree language.[12]
Geography
As Saskatchewan's borders largely follow the geographic coordinates of longitude and latitude, the province is roughly a quadrilateral, or a shape with four sides. However, the 49th parallel boundary and the 60th northern border appear curved on globes and many maps. Additionally, the eastern boundary of the province is partially crooked rather than following a line of longitude, as correction lines were devised by surveyors prior to the homestead program (1880–1928).

Topographic map of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is part of the Western Provinces and is bounded on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the north-east by Nunavut, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan has the distinction of being the only Canadian province for which no borders correspond to physical geographic features (i.e. they are all parallels and meridians). Along with Alberta, Saskatchewan is one of only two land-locked provinces.
The overwhelming majority of Saskatchewan's population is located in the southern third of the province, south of the 53rd parallel.
Saskatchewan contains two major natural regions: the Canadian Shield in the north and the Interior Plains in the south. Northern Saskatchewan is mostly covered by boreal forest except for the Lake Athabasca Sand Dunes, the largest active sand dunes in the world north of 58°, and adjacent to the southern shore of Lake Athabasca. Southern Saskatchewan contains another area with sand dunes known as the "Great Sand Hills" covering over 300 square kilometres (120 sq mi). The Cypress Hills, located in the southwestern corner of Saskatchewan and Killdeer Badlands (Grasslands National Park), are areas of the province that were unglaciated during the last glaciation period, the Wisconsin glaciation.
The province's highest point, at 1,392 metres (4,567 ft), is located in the Cypress Hills less than 2 km from the provincial boundary with Alberta.[13] The lowest point is the shore of Lake Athabasca, at 213 metres (699 ft). The province has 14 major drainage basins made up of various rivers and watersheds draining into the Arctic Ocean, Hudson Bay and the Gulf of Mexico.[14]
Climate

Köppen climate types of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan receives more hours of sunshine than any other Canadian province.[15] The province lies far from any significant body of water. This fact, combined with its northerly latitude, gives it a warm summer, corresponding to its humid continental climate (Köppen type Dfb) in the central and most of the eastern parts of the province, as well as the Cypress Hills; drying off to a semi-arid steppe climate (Köppen type BSk) in the southwestern part of the province. Drought can affect agricultural areas during long periods with little or no precipitation at all. The northern parts of Saskatchewan – from about La Ronge northward – have a subarctic climate (Köppen Dfc) with a shorter summer season. Summers can get very hot, sometimes above 38 °C (100 °F) during the day, and with humidity decreasing from northeast to southwest. Warm southern winds blow from the plains and intermontane regions of the Western United States during much of July and August, very cool or hot but changeable air masses often occur during spring and in September. Winters are usually bitterly cold, with frequent Arctic air descending from the north.[16] with high temperatures not breaking −17 °C (1 °F) for weeks at a time. Warm chinook winds often blow from the west, bringing periods of mild weather. Annual precipitation averages 30 to 45 centimetres (12 to 18 inches) across the province, with the bulk of rain falling in June, July, and August.[17]
Saskatchewan is one of the most tornado-active parts in Canada, averaging roughly 12 to 18 tornadoes per year, some violent. In 2012, 33 tornadoes were reported in the province. The Regina Cyclone took place in June 1912 when 28 people died in an F4 Fujita scale tornado. Severe and non-severe thunderstorm events occur in Saskatchewan, usually from early spring to late summer. Hail, strong winds and isolated tornadoes are a common occurrence.
The hottest temperature ever recorded anywhere in Canada happened in Saskatchewan. The temperature rose to 45 °C (113 °F) in Midale and Yellow Grass. The coldest ever recorded in the province was −56.7 °C (−70.1 °F) in Prince Albert, which is north of Saskatoon.
| City | July (°C) | July (°F) | January (°C) | January (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maple Creek | 27/11 | 81/52 | −5/−16 | 23/4 |
| Estevan | 27/13 | 81/55 | −9/−20 | 16/−4 |
| Weyburn | 26/12 | 79/54 | −10/−21 | 14/−6 |
| Moose Jaw | 26/12 | 79/54 | −8/−19 | 18/−2 |
| Regina | 26/11 | 79/52 | −10/−22 | 14/−8 |
| Saskatoon | 25/11 | 77/52 | −12/−22 | 10/−8 |
| Melville | 25/11 | 77/52 | −12/−23 | 10/−9 |
| Swift Current | 25/11 | 77/52 | −7/−17 | 19/1 |
| Humboldt | 24/11 | 75/52 | −12/−23 | 10/−9 |
| Melfort | 24/11 | 75/52 | −14/−23 | 7/−9 |
| North Battleford | 24/11 | 75/52 | −12/−22 | 10/−8 |
| Yorkton | 24/11 | 75/52 | −13/−23 | 9/−9 |
| Lloydminster | 23/11 | 73/52 | −10/−19 | 14/−2 |
| Prince Albert | 24/11 | 75/52 | −13/−25 | 9/−13 |
History

Henry Kelsey sees a buffalo herd on the western plains.
Saskatchewan has been populated by various indigenous peoples of North America, including members of the Sarcee, Niitsitapi, Atsina, Cree, Saulteaux, Assiniboine (Nakoda), Lakota and Sioux. The first known European to enter Saskatchewan was Henry Kelsey in 1690, who travelled up the Saskatchewan River in hopes of trading fur with the region's indigenous peoples. The first permanent European settlement was a Hudson's Bay Company post at Cumberland House, founded in 1774 by Samuel Hearne.[19] In 1762 the south of the province was part of the Spanish Louisiana until 1802.[20]
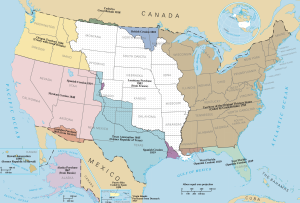
Part of Alberta and Saskatchewan were traded from the United States, which in return received part of Rupert's Land, today part of North Dakota and Minnesota.

Cree Pipe Stem Carrier, a painting of a Plains Cree warrior by Paul Kane.
In 1803 the Louisiana Purchase transferred from France to the United States part of what is now Alberta and Saskatchewan. In 1818 the U.S. ceded the area to Britain. Most of what is now Saskatchewan was part of Rupert's Land and controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which claimed rights to all watersheds flowing into Hudson Bay, including the Saskatchewan River, Churchill, Assiniboine, Souris, and Qu'Appelle River systems.
In the late 1850s and early 1860s, scientific expeditions led by John Palliser and Henry Youle Hind explored the prairie region of the province.
In 1870, Canada acquired the Hudson's Bay Company's territories and formed the North-West Territories to administer the vast territory between British Columbia and Manitoba. The Crown also entered into a series of numbered treaties with the indigenous peoples of the area, which serve as the basis of the relationship between First Nations, as they are called today, and the Crown. Since the late twentieth century, land losses and inequities as a result of those treaties have been subject to negotiation for settlement between the First Nations in Saskatchewan and the federal government, in collaboration with provincial governments.
In 1876, following their defeat of United States Army forces at the Battle of the Little Bighorn in Montana Territory in the United States, the Lakota Chief Sitting Bull led several thousand of his people to Wood Mountain. Survivors and descendants founded Wood Mountain Reserve in 1914.

The Battle of Batoche, 1885
The North-West Mounted Police set up several posts and forts across Saskatchewan, including Fort Walsh in the Cypress Hills, and Wood Mountain Post in south-central Saskatchewan near the United States border.
Many Métis people, who had not been signatories to a treaty, had moved to the Southbranch Settlement and Prince Albert district north of present-day Saskatoon following the Red River Rebellion in Manitoba in 1870. In the early 1880s, the Canadian government refused to hear the Métis' grievances, which stemmed from land-use issues. Finally, in 1885, the Métis, led by Louis Riel, staged the North-West Rebellion and declared a provisional government. They were defeated by a Canadian militia brought to the Canadian prairies by the new Canadian Pacific Railway. Riel, who surrendered and was convicted of treason in a packed Regina courtroom, was hanged on November 16, 1885. Since then, the government has recognized the Métis as an aboriginal people with status rights and provided them with various benefits.
European settlements
National policy set by the federal government, the Canadian Pacific Railway, the Hudson's Bay Company and associated land companies encouraged immigration. The Dominion Lands Act of 1872 permitted settlers to acquire one quarter of a square mile of land to homestead and offered an additional quarter upon establishing a homestead. In 1874, the North-West Mounted Police began providing police services. In 1876, the North-West Territories Act provided for appointment, by the Ottawa, of a Lieutenant Governor and a Council to assist him.[21]
Highly optimistic advertising campaigns promoted the benefits of prairie living. Potential immigrants read leaflets information painted Canada as a veritable garden of Eden, and downplayed the need for agricultural expertise. Ads in The Nor'-West Farmer by the Commissioner of Immigration implied that western land was blessed with water, wood, gold, silver, iron, copper, and cheap coal for fuel, all of which were readily at hand. Reality was far harsher, especially for the first arrivals who lived in sod houses. However eastern money poured in and by 1913, long term mortgage loans to Saskatchewan farmers had reached $65 million.[22]
The dominant groups comprised British settlers from eastern Canada and Britain, who comprised about half of the population during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. They played the leading role in establishing the basic institutions of plains society, economy and government.[23]
Gender roles were sharply defined. Men were primarily responsible for breaking the land; planting and harvesting; building the house; buying, operating and repairing machinery; and handling finances. At first there were many single men on the prairie, or husbands whose wives were still back east, but they had a hard time. They realized the need for a wife. In 1901, there were 19,200 families, but this surged to 150,300 families only 15 years later. Wives played a central role in settlement of the prairie region. Their labor, skills, and ability to adapt to the harsh environment proved decisive in meeting the challenges. They prepared bannock, beans and bacon, mended clothes, raised children, cleaned, tended the garden, helped at harvest time and nursed everyone back to health. While prevailing patriarchal attitudes, legislation, and economic principles obscured women's contributions, the flexibility exhibited by farm women in performing productive and nonproductive labor was critical to the survival of family farms, and thus to the success of the wheat economy.[24]
Immigration peaked in 1910, and in spite of the initial difficulties of frontier life – distance from towns, sod homes, and backbreaking labour – new settlers established a European-Canadian style of prosperous agrarian society.
20th century
On September 1, 1905, Saskatchewan became a province, with inauguration day held September 4. Its political leaders at the time proclaimed its destiny was to become Canada's most powerful province. Saskatchewan embarked on an ambitious province-building program based on its Anglo-Canadian culture and wheat production for the export market. Population quintupled from 91,000 in 1901 to 492,000 to 1911, thanks to heavy immigration of farmers from the Ukraine, U.S., Germany and Scandinavia. Efforts were made to assimilate the newcomers to British Canadian culture and values.[25]
The long-term prosperity of the province depended on the world price of grain, which headed steadily upward from the 1880s to 1920, then plunged down. Wheat output was increased by new strains, such as the "Marquis wheat" strain which matured 8 days sooner and yielded 7 more bushels per acre than the previous standard, "Red Fife". The national output of wheat soared from 8 million bushels in 1896, to 26 million in 1901, reaching 151 million by 1921.[26]
In the 1905 provincial elections, Liberals won 16 of 25 seats in Saskatchewan. The Saskatchewan government bought out Bell Telephone Company in 1909, with the government owning the long-distance lines and left local service to small companies organized at the municipal level.[27] Premier Walter Scott preferred government assistance to outright ownership because he thought enterprises worked better if citizens had a stake in running them; he set up the Saskatchewan Cooperative Elevator Company in 1911. Despite pressure from farm groups for direct government involvement in the grain handling business, the Scott government opted to loan money to a farmer-owned elevator company. Saskatchewan in 1909 provided bond guarantees to railway companies for the construction of branch lines, alleviating the concerns of farmers who had trouble getting their wheat to market by wagon.[28] The Saskatchewan Grain Growers Association, was the dominant political force in the province until the 1920s; it had close ties with the governing Liberal party. In 1913, the Saskatchewan Stock Growers Association was established with three goals: to watch over legislation; to forward the interests of the stock growers in every honourable and legitimate way; and to suggest to parliament legislation to meet changing conditions and requirements.[29]
Urban reform movements in Regina were based on support from business and professional groups. City planning, reform of local government, and municipal ownership of utilities were more widely supported by these two groups, often through such organizations as the Board of Trade. Church-related and other altruistic organizations generally supported social welfare and housing reforms; these groups were generally less successful in getting their own reforms enacted.[30]
1914–39
The province responded to the First World War in 1914 with patriotic enthusiasm and enjoyed the resultant economic boom for farms and cities alike. Emotional and intellectual support for the war emerged from the politics of Canadian national identity, the rural myth, and social gospel progressivism The Church of England was especially supportive. However, there was strong hostility toward German-Canadian farmers.[31] Recent Ukrainian immigrants were enemy aliens because of their citizenship in the Austro-Hungarian Empire. A small fraction were taken to internment camps. Most of the internees were unskilled unemployed labourers who were imprisoned "because they were destitute, not because they were disloyal."[32][33]
The price of wheat tripled and acreage seeded doubled. The wartime spirit of sacrifice intensified social reform movements that had predated the war and now came to fruition. Saskatchewan gave women the right to vote in 1916 and at the end 1916 passed a referendum to prohibit the sale of alcohol.

Bennett buggies, automobiles pulled by horses, were used during the Great Depression by farmers with too little cash to purchase gasoline.
In the late 1920s, the Ku Klux Klan, imported from the United States and Ontario, gained brief popularity in nativist circles in Saskatchewan and Alberta. The Klan, briefly allied with the provincial Conservative party because of their mutual dislike for Premier James G. "Jimmy" Gardiner and his Liberals (who ferociously fought the Klan), enjoyed about two years of prominence. It declined and disappeared, subject to widespread political and media opposition, plus internal scandals involving the use of the organization's funds.
Recent history
In 1970, the first annual Canadian Western Agribition was held in Regina. This farm-industry trade show, with its strong emphasis on livestock, is rated as one of the five top livestock shows in North America, along with those in Houston, Denver, Louisville and Toronto.
The province celebrated the 75th anniversary of its establishment in 1980, with Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon, presiding over the official ceremonies.[34][35] In 2005, 25 years later, her sister, Queen Elizabeth II, attended the events held to mark Saskatchewan's centennial.[36]
Since the late 20th century, First Nations have become more politically active in seeking justice for past inequities, especially related to government taking of indigenous lands. The federal and provincial governments have negotiated on numerous land claims, and developed a program of "Treaty Land Entitlement", enabling First Nations to buy land to be taken into reserves with money from settlements of claims.
"In 1992, the federal and provincial governments signed an historic land claim agreement with Saskatchewan First Nations. Under the Agreement, the First Nations received money to buy land on the open market. As a result, about 761,000 acres have been turned into reserve land and many First Nations continue to invest their settlement dollars in urban areas", including Saskatoon. The money from such settlements has enabled First Nations to invest in businesses and other economic infrastructure.[11]
Demographics
According to the Canada 2011 Census, the largest ethnic group in Saskatchewan is German (28.6%), followed by English (24.9%), Scottish (18.9%), Canadian (18.8%), Irish (15.5%), Ukrainian (13.5%), French (Fransaskois) (12.2%), First Nations (12.1%), Norwegian (6.9%), and Polish (5.8%).[37]

Saskatchewan's population since 1901
| Year | Population | Five-year % change | Ten-year % change | Rank among provinces |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 91,279 | n/a | n/a | 8 |
| 1911 | 492,432 | n/a | 439.5 | 3 |
| 1921 | 757,510 | n/a | 53.8 | 3 |
| 1931 | 921,785 | n/a | 21.7 | 3 |
| 1941 | 895,992 | n/a | −2.8 | 3 |
| 1951 | 831,728 | n/a | −7.2 | 5 |
| 1956 | 880,665 | 5.9 | n/a | 5 |
| 1961 | 925,181 | 5.1 | 11.2 | 5 |
| 1966 | 955,344 | 3.3 | 8.5 | 6 |
| 1971 | 926,242 | −3.0 | 0.1 | 6 |
| 1976 | 921,325 | −0.5 | 3.6 | 6 |
| 1981 | 968,313 | 5.1 | 4.5 | 6 |
| 1986 | 1,009,613 | 4.3 | 9.6 | 6 |
| 1991 | 988,928 | −2.0 | 2.1 | 6 |
| 1996 | 976,615 | −1.2 | −3.3 | 6 |
| 2001 | 978,933 | 0.2 | −1.0 | 6 |
| 2006 | 985,386 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 6 |
| 2011 | 1,053,960 | 7.0 | 7.6 | 6 |
| 2016 | 1,098,352 | 6.3 | 11.4 | 6 |
[38][39]
The largest denominations by number of adherents according to the 2001 census were the Roman Catholic Church with 286,815 (30%); the United Church of Canada with 187,450 (20%); and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Canada with 78,520 (8%). 148,535 (15.4%) responded "no religion".[40]
Municipalities
Ten largest municipalities by population
| Municipality | 2001 | 2006 | 2011 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Saskatoon | 196,861 | 202,340 | 222,189 | 246,376 |
Regina | 178,225 | 179,246 | 193,100 | 215,106 |
Prince Albert | 34,291 | 34,138 | 35,129 | 35,926 |
Moose Jaw | 32,131 | 32,132 | 33,274 | 33,890 |
Swift Current | 14,821 | 14,946 | 15,503 | 16,604 |
Yorkton | 15,107 | 15,038 | 15,669 | 16,343 |
North Battleford | 13,692 | 13,190 | 13,888 | 14,315 |
Estevan | 10,242 | 10,084 | 11,054 | 11,483 |
Warman | 3,481 | 4,764 | 7,104 | 11,020 |
Weyburn | 9,534 | 9,433 | 10,484 | 10,870 |
This list does not include Lloydminster, which has a total population of 31,410 but straddles the Alberta–Saskatchewan border. As of 2016, 11,765 people lived on the Saskatchewan side, which would make it Saskatchewan's 8th largest municipality. All of the listed communities are considered cities by the province; municipalities in the province with a population of 5,000 or more can receive official city status.
Economy

Fields of canola and flax on the Saskatchewan Prairie.
Historically, Saskatchewan's economy was primarily associated with agriculture. However, increasing diversification has resulted in agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting only making up 6.8% of the province's GDP. Saskatchewan grows a large portion of Canada's grain.[41]Wheat is the most familiar crop and the one most often associated with the province (there are sheafs of wheat depicted on the coat of arms of Saskatchewan), but other grains like canola, flax, rye, oats, peas, lentils, canary seed, and barley are also produced. Saskatchewan is the world's largest exporter of mustard seed.[42]Beef cattle production by a Canadian province is only exceeded by Alberta. In the northern part of the province, forestry is also a significant industry.
Mining is a major industry in the province, with Saskatchewan being the world's largest exporter of potash and uranium.[43]
Oil and natural gas production is also a very important part of Saskatchewan's economy, although the oil industry is larger. Among Canadian provinces, only Alberta exceeds Saskatchewan in overall oil production.[44] Heavy crude is extracted in the Lloydminster-Kerrobert-Kindersley areas. Light crude is found in the Kindersley-Swift Current areas as well as the Weyburn-Estevan fields. Natural gas is found almost entirely in the western part of Saskatchewan, from the Primrose Lake area through Lloydminster, Unity, Kindersley, Leader, and around Maple Creek areas.[45]
Saskatchewan's GDP in 2006 was approximately C$45.922 billion,[46] with economic sectors breaking down in the following way:
| % | Sector |
|---|---|
| 17.1 | finance, insurance, real estate, leasing |
| 13.0 | mining, petroleum |
| 11.9 | education, health, social services |
| 11.7 | wholesale and retail trade |
| 9.1 | transportation, communications, utilities |
| 7.7 | manufacturing |
| 6.8 | agriculture, forestry, fishing, hunting |
| 6.5 | business services |
| 5.8 | government services |
| 5.1 | construction |
| 5.3 | other |
A list of the top 100 companies includes The Potash Corporation of Saskatchewan (defunct in December 2017), Federated Cooperatives Ltd. and IPSCO.
Major Saskatchewan-based Crown corporations are Saskatchewan Government Insurance (SGI), SaskTel, SaskEnergy (the province's main supplier of natural gas), and SaskPower. Bombardier runs the NATO Flying Training Centre at 15 Wing, near Moose Jaw. Bombardier was awarded a long-term contract in the late 1990s for $2.8 billion from the federal government for the purchase of military aircraft and the running of the training facility. SaskPower since 1929 has been the principal supplier of electricity in Saskatchewan, serving more than 451,000 customers and managing $4.5 billion in assets. SaskPower is a major employer in the province with almost 2,500 permanent full-time staff located in 71 communities.
Provincial finances
| Fiscal Year | Population1 | Gov't Debt2 | Crown Debt3 | Budget Surplus | GFSF Balance | Pers. Inc. Tax Revenue | Corp. Inc. Tax Revenue4 | PST Revenue5 | Resource Revenue | Health Expense | Credit Rating6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015–2016 | 1,134,402 | 4,798,562 | 7,589,001 | −1,520,000 | 0 | 2,537,349 | 1,002,546 | 1,288,921 | 1,761,265 | 5,109,545 | AAA (neg) |
| 2014–2015 | 1,122,588 | 3,799,970 | 6,892,757 | 62,000 | 131,269 | 2,546,577 | 848,469 | 1,358,205 | 2,614,478 | 4,981,636 | AAA |
| 2013–2014 | 1,093,880 | 3,803,006 | 5,955,899 | 589,000 | 446,269 | 2,470,056 | 1,017,188 | 1,326,403 | 2,520,964 | 4,834,932 | AAA |
| 2012–2013 | 1,073,107 | 3,804,817 | 4,981,693 | 16,000 | 666,000 | 2,406,254 | 838,275 | 1,284,893 | 2,515,869 | 4,575,589 | AAA |
| 2011–2012 | 1,053,960 | 3,807,590 | 4,193,541 | 55,000 | 708,000 | 1,897,409 | 793,790 | 1,322,161 | 2,821,957 | 4,400,159 | AAA |
| 2010–2011 | 1,041,729 | 4,135,226 | 3,744,627 | 96,000 | 1,006,000 | 1,795,788 | 1,155,273 | 1,186,922 | 2,527,799 | 4,202,106 | AA+ |
| 2009–2010 | 1,025,638 | 4,140,482 | 3,618,953 | 167,705 | 958,000 | 1,890,848 | 881,424 | 1,084,001 | 1,910,624 | 3,934,231 | AA+ |
| 2008–2009 | 1,010,218 | 4,145,286 | 3,390,175 | 1,969,933 | 1,215,000 | 1,844,226 | 591,930 | 1,108,628 | 4,612,408 | 3,976,241 | AA+ |
| 2007–2008 | 996,130 | 6,824,323 | 3,172,903 | 1,282,869 | 1,528,934 | 1,938,258 | 673,641 | 995,995 | 2,325,116 | 3,504,333 | AA |
| 2006–2007 | 991,260 | 7,244,938 | 3,398,647 | 397,794 | 887,500 | 1,668,538 | 1,067,459 | 1,079,794 | 1,694,252 | 3,202,965 | AA |
| 2005–2006 | 994,996 | 7,197,223 | 3,444,783 | 539,466 | 887,500 | 1,447,905 | 918,279 | 1,112,350 | 1,721,100 | 2,990,625 | AA |
| 2004–2005 | 997,263 | 7,545,574 | 3,319,737 | 765,117 | 748,500 | 1,329,081 | 638,968 | 985,079 | 1,474,191 | 2,773,961 | AA- |
| 2003–2004 | 995,848 | 8,031,637 | 3,171,093 | −210,017 | 366,000 | 1,245,763 | 682,052 | 854,480 | 1,140,962 | 2,515,823 | AA- |
| 2002–2003 | 997,805 | 7,821,426 | 3,084,579 | 82,860 | 577,000 | 1,429,757 | 557,360 | 813,932 | 1,243,649 | 2,342,835 | A+ |
| 2001–2002 | 1,001,643 | 7,561,899 | 3,166,992 | −278,902 | 495,000 | 1,196,410 | 507,542 | 770,984 | 903,044 | 2,199,723 | A+ |
The Tabulated Data covers each fiscal year (e.g. 2015–2016 covers April 1, 2015 – March 31, 2016).
All data is in $1,000s.
1 These values reflect the estimated population at the beginning of the fiscal year.
2 These values reflect the debt of the General Revenue Fund alone at the end of the fiscal year.
3 These values reflect the combined debt of the three major Government Service Enterprises (Crown Corporations) at the end of the fiscal year. As of March 31, 2016, SaskPower, SaskEnergy, and SaskTel accounted for 88.4% of Crown Debt.
4 The highest rate of provincial corporate income tax was reduced from 17% to 14% on July 1, 2006. It was further reduced to 13% on July 1, 2007, and finally to 12% on July 1, 2008. The tax on paid-up capital was reduced from 0.6% to 0.3% on July 1, 2006, to 0.15% on July 1, 2007, and abolished altogether on July 1, 2008. These displayed values were obtained by adding the corporate income tax for each year with the corporate capital tax.
5 The Provincial Sales Tax (PST) rate was reduced from 7% to 5% on October 28, 2006.
6 These values are the credit ratings from Standard & Poor's as of the end of the Fiscal Year.
Source: Government of Saskatchewan.[47]
Government and politics
Saskatchewan has the same form of government[48] as the other Canadian provinces with a lieutenant-governor (who is the representative of the Queen in Right of Saskatchewan), premier, and a unicameral legislature.
For many years, Saskatchewan was one of Canada's more progressive provinces, reflecting many of its citizens' feelings of alienation from the interests of large capital. In 1944 Tommy Douglas became premier of the first avowedly socialist regional government in North America. Most of his Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs) represented rural and small-town ridings. Under his Cooperative Commonwealth Federation government, Saskatchewan became the first province to have Medicare. In 1961, Douglas left provincial politics to become the first leader of the federal New Democratic Party.
Provincial politics in Saskatchewan is dominated by the social-democratic New Democrats and the centre-right Saskatchewan Party, with the latter holding the majority in the Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan since 2007. Numerous smaller political parties also run candidates in provincial elections, including the Green Party, Liberal Party, and the Progressive Conservative Party, but none is currently represented in the Legislative Assembly (Liberals and Conservatives generally caucus under the Saskatchewan Party banner in provincial affairs). After 16 years of New Democratic governments under premiers Roy Romanow and Lorne Calvert, the 2007 provincial election was won by the Saskatchewan Party under Brad Wall. In the 2011 election, Premier Wall and the Saskatchewan Party were returned with an increased majority.
Recent federal elections have been dominated by the Conservative Party since the party currently represents 10 of 14 federal ridings in Saskatchewan, while the New Democratic Party represents three and the Liberal Party of Canada, one.
Law enforcement
- Police agencies
- Saskatchewan Highway Patrol
- Canadian Forces Military Police (15 Wing Moose Jaw / CFD Dundurn)
- Canadian National Railway Police Service
- Canadian Pacific Railway Police Service
- Caronport Police Service
- Corman Park Police Service
- Dalmeny Police Service
- Estevan Police Service
- File Hills First Nation Police Service
Global Transportation Hub Enforcement (Special Constables)- Luseland Police Service
- Moose Jaw Police Service
- Prince Albert Police Service
- Regina Police Service
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police
- Saskatchewan Conservation Officer (Special Constables)
- Saskatoon Police Service
University of Regina Security (Special Constables)
University of Saskatchewan Department of Campus Safety (Special Constables)- Vanscoy Police Service
Wascana Centre Police (Special Constables)- Weyburn Police Service
- Wilton Police Service
- Correctional facilities
- Pine Grove Correctional Centre
- Prince Albert Correctional Centre
- Regina Correctional Centre
- Regina Paul Dojack Youth Centre
- Saskatchewan Penitentiary
- Saskatoon correctional centre
- Regional Psychiatric Centre
- Saskatoon Kilburn Hall
Education
The first education on the prairies took place within the family groups of the First Nation and early fur trading settlers. There were only a few missionary or trading post schools established in Rupert's Land – later known as the North West Territories.
The first 76 North-West Territories school districts and the first Board of Education meeting formed in 1886. The pioneering boom formed ethnic bloc settlements. Communities were seeking education for their children similar to the schools of their home land. Log cabins, and dwellings were constructed for the assembly of the community, school, church, dances and meetings.
The prosperity of the Roaring Twenties and the success of farmers in proving up on their homesteads helped provide funding to standardize education.[citation needed] Text books, normal schools for educating teachers, formal school curricula and state of the art school house architectural plans provided continuity throughout the province. English as the school language helped to provide economic stability, because one community could communicate with another and goods could be traded and sold in a common language. The number of one-room school house districts across Saskatchewan totalled approximately 5,000 at the height of this system of education in the late 1940s.[49]
Following World War II, the transition from many one-room school houses to fewer and larger consolidated modern technological town and city schools occurred as a means of ensuring technical education. School buses, highways, and family vehicles create ease and accessibility of a population shift to larger towns and cities. Combines and tractors mean the farmer could manage more than a quarter section of land, so there was a shift from family farms and subsistence crops to cash crops grown on many sections of land.
School vouchers have been newly proposed as a means of allowing competition between rural schools and making the operation of co-operative schools practicable in rural areas.
Healthcare
Saskatchewan's Ministry of Health is responsible for policy direction, sets and monitors standards, and provides funding for regional health authorities and provincial health services.
| Wikinews has related news: Canada pursues new nuclear research reactor to produce medical isotopes |
Saskatchewan's medical health system is widely and inaccurately characterized as "socialized medicine": medical practitioners in Saskatchewan, as in other Canadian provinces, are not civil servants but remit their accounts to the publicly funded Saskatchewan Medical Care Insurance Plan rather than to patients (i.e. a single-payer system).[50]
Saskatchewan medical health system has faced criticism due to a lack of accessibility to the midwifery program. According to Leanne Smith, the director for maternal services in the Saskatoon Health Region declared half of the women who apply for the midwifery program are turned away.[51] Ministry of Health data shows midwives saw 1,233 clients in the 2012–13 fiscal year (which runs April to March). But in that fourth quarter, 359 women were still on waiting lists for immediate or future care.[51] The provincial Health Ministry received 47 letters about midwifery services in 2012, most of which asked for more midwives.[51] As a continuing problem in the Saskatchewan health care system, more pressure has been placed to recruit more midwives for the province.
Transportation

Trans Canada 1

Eatonia Railway Station
Transportation in Saskatchewan includes an infrastructure system of roads, highways, freeways, airports, ferries, pipelines, trails, waterways and railway systems serving a population of approximately 1,003,299 (according to 2007 estimates) inhabitants year-round. It is funded primarily with local and federal government funds. The Saskatchewan Department of Highways and Transportation estimates 80% of traffic is carried on the 5,031-kilometre principal system of highways.[52]
The Ministry of Highways and Infrastructure operates over 26,000 kilometres (16,000 mi) of highways and divided highways. There are also municipal roads which comprise different surfaces. Asphalt concrete pavements comprise almost 9,000 kilometres (5,600 mi), granular pavement almost 5,000 kilometres (3,100 mi), non structural or thin membrane surface TMS are close to 7,000 kilometres (4,300 mi) and finally gravel highways make up over 5,600 kilometres (3,500 mi) through the province. In the northern sector, ice roads which can only be navigated in the winter months comprise another approximately 150 kilometres (93 mi) of travel.[53]
Saskatchewan has over 250,000 kilometres (150,000 mi) of roads and highways, the highest amount of road surface of any Canadian province.[54] The major highways in Saskatchewan are the Trans Canada expressway, Yellowhead Highway northern Trans Canada route, Louis Riel Trail, CanAm Highway, Red Coat Trail, Northern Woods and Water route, and Saskota travel route.
The first Canadian transcontinental railway was constructed by the Canadian Pacific Railway between 1881 and 1885.[55] After the great east-west transcontinental railway was built, north-south connector branch lines were established.
The 1920s saw the largest rise in rail line track as the CPR and CNR fell into competition to provide rail service within ten kilometres. In the 1960s there were applications for abandonment of branch lines.[56] Today the only two passenger rail services in the province are The Canadian and Winnipeg–Churchill train, both operated by Via Rail. The Canadian is a transcontinental service linking Toronto with Vancouver.
The main Saskatchewan waterways are the North Saskatchewan River or South Saskatchewan River routes. In total, there are 3,050 bridges maintained by the Department of Highways in Saskatchewan.[57] There are currently twelve ferry services operating in the province, all under the jurisdiction of the Department of Highways.
| Ferry | Location | Waterway | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
Estuary | connecting Estuary and Laporte | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Lemsford | North of Lemsford connecting 32 and 30 | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Lancer | North of Lancer connecting 32 and 30 | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Riverhurst | Highway 42 and Highway 373 | Lake Diefenbaker | [58] |
Clarkboro | Between Warman and Aberdeen on 784 | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Hague | Between Hague and Aberdeen | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
St. Laurent | East of Duck Lake, 11 and Batoche 225 | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Fenton | Between 25 and 3 on Grid Road | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Weldon | Between 3, Weldon via 682 and 302, Prince Albert | South Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Paynton | Between 16 and 26 via 764 | North Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Wingard | East of Marcelin, 40 connecting to 11 Wingard | North Saskatchewan River | [58] |
Cecil | Between 302 and 55 east of Prince Albert | North Saskatchewan River | [58] |
The Saskatoon Airport (YXE) was initially established as part of the Royal Canadian Air Force training program during World War II. It was renamed the John G. Diefenbaker Airport in the official ceremony, June 23, 1993.[59]Roland J. Groome Airfield is the official designation for the Regina International Airport (YQR) as of August 3, 2005; the airport was established in 1930. Under the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (BCATP),[60] twenty Service Flying Training Schools (RAF) were established at various Saskatchewan locations in World War II.[61] 15 Wing Moose Jaw is home to the Canadian Forces formation aerobatics team, the Snowbirds.[60]
Airlines offering service to Saskatchewan are Air Canada, WestJet Airlines, United Airlines, Delta Air Lines, Transwest Air, Sunwing Airlines, Norcanair Airlines, La Ronge Aviation Services Ltd, La Loche Airways, Osprey Wings Ltd, Buffalo Narrows Airways Ltd, Île-à-la-Crosse Airways Ltd, Voyage Air, Pronto Airways, Venture Air Ltd, Pelican Narrows Air Service, Jackson Air Services Ltd, and Northern Dene Airways Ltd.[62]
The Government of Canada has agreed to contribute $20 million for two new interchanges in Saskatoon. One of them being at the Sk Hwy 219 / Lorne Ave intersection with Circle Drive, the other at the Senator Sid Buckwold Bridge (Idylwyld Freeway) and Circle Drive. This is part of the Asia-Pacific Gateway and Corridor Initiative to improve access to the Canadian National Railway's intermodal freight terminal thereby increasing Asia-Pacific trade. Also, the Government of Canada will contribute $27 million to Regina to construct a Canadian Pacific Railway CPR intermodal facility and improve infrastructure transportation to the facility from both national highway networks, Sk Hwy 1, the TransCanada Highway and Sk Hwy 11, Louis Riel Trail. This also is part of the Asia-Pacific Gateway and Corridor Initiative to improve access to the CPR terminal and increase Asia-Pacific trade.[63]
Arts and culture
- Museums and galleries
- MacKenzie Art Gallery
- Remai Modern
- RCMP Heritage Centre
- Saskatchewan Western Development Museum
- Orchestras
- Regina Symphony Orchestra
- Saskatoon Symphony Orchestra
- Artist-run centres
- PAVED Arts
- Artists
Joe Fafard, sculptor
Sports
The Saskatchewan Roughriders Canadian football team is the province's professional football franchise, and are extremely popular across Saskatchewan. The team's fans are also found to congregate on game days throughout Canada, and collectively they are known as "Rider Nation".
The province's other major sport franchise is the Saskatchewan Rush of the National Lacrosse League. In their first year of competition, 2016, the Rush won both their Division Title and the League Championship.
Hockey is the most popular sport in the province. More than 490 NHL players[64] have been born in Saskatchewan, the highest per capita output of any Canadian province, U.S. state, or European country.[65] Notable NHL figures born in Saskatchewan include Keith Allen, Gordie Howe, Bryan Trottier, Bernie Federko, Clark Gillies, Fern Flaman, Bert Olmstead, Harry Watson, Elmer Lach, Max Bentley, Sid Abel, Doug Bentley, Eddie Shore, Clint Smith, Bryan Hextall, Johnny Bower, Emile Francis, Glenn Hall, Chuck Rayner, Brad McCrimmon, Patrick Marleau, Dave Manson, Theo Fleury, Terry Harper, Wade Redden, Brian Propp, Scott Hartnell, Ryan Getzlaf, and Chris Kunitz. Saskatchewan does not have an NHL or minor professional franchise, but five teams in the junior Western Hockey League are located in the province: the Moose Jaw Warriors, Prince Albert Raiders, Regina Pats, Saskatoon Blades and Swift Current Broncos.
In 2015, Budweiser honoured Saskatchewan for their abundance of hockey players by sculpting a 12-foot-tall hockey player monument in ice for Saskatchewan’s capital city of Regina.[66] The company then filmed this frozen monument for a national television commercial, thanking the province for creating so many goal scorers throughout hockey’s history. Budweiser also gifted the “hockey player” province a trophy made of white birch—Saskatchewan’s provincial tree—which bears the name of every pro player in history. Sitting atop the trophy was a golden Budweiser Red Light, synched to every current Saskatchewan player in the pros. This trophy can currently be seen at Victoria Bar in Regina.
Provincial symbols

The official tartan of Saskatchewan, created in 1961.
The flag of Saskatchewan was officially adopted on September 22, 1969.[67] The flag features the provincial shield in the upper quarter nearest the staff, with the floral emblem, the Prairie Lily, in the fly. The upper green (in forest green) half of the flag represents the northern Saskatchewan forest lands, while the golden lower half of the flag symbolizes the southern wheat fields and prairies. A province-wide competition was held to design the flag, and drew over 4,000 entries. The winning design was by Anthony Drake, then living in Hodgeville.[68]
In 2005, Saskatchewan Environment held a province-wide vote to recognize Saskatchewan's centennial year, receiving more than 10,000 on-line and mail-in votes from the public. The walleye was the overwhelming favourite of the six native fish species nominated for the designation, receiving more than half the votes cast.[69] Other species in the running were the lake sturgeon, lake trout, lake whitefish, northern pike and yellow perch.
Saskatchewan's other symbols include the tartan, the license plate, and the provincial flower. Saskatchewan's official tartan was registered with the Court of Lord Lyon King of Arms in Scotland in 1961. It has seven colours: gold, brown, green, red, yellow, white and black. The provincial licence plates display the slogan "Land of Living Skies". The provincial flower of Saskatchewan is the Western Red Lily.
Centennial celebrations
In 2005, Saskatchewan celebrated its centennial. To honour it, the Royal Canadian Mint issued a commemorative five-dollar coin depicting Canada's wheat fields as well as a circulation 25-cent coin of a similar design. Queen Elizabeth II and the Duke of Edinburgh visited Regina, Saskatoon, and Lumsden, and the Saskatchewan-reared Joni Mitchell issued an album in Saskatchewan's honour.
Climate
The effects of climate change in Saskatchewan are now being observed in parts of the province. There is evidence of reduction of biomass in Saskatchewan's boreal forests[citation needed] (as with those of other Canadian prairie provinces) is linked by researchers to drought-related water stress, stemming from global warming, most likely caused by greenhouse gas emissions. While studies, as early as 1988 (Williams, et al., 1988) have shown climate change will affect agriculture,[70] whether the effects can be mitigated through adaptations of cultivars, or crops, is less clear. Resiliency of ecosystems may decline with large changes in temperature.[71] The provincial government has responded to the threat of climate change by introducing a plan to reduce carbon emissions, "The Saskatchewan Energy and Climate Change Plan," in June 2007.
See also
- Outline of Saskatchewan
Index of Saskatchewan-related articles
References
^ "Emblems of Saskatchewan". Government of Saskatchewan. Archived from the original on March 17, 2015. Retrieved July 22, 2014..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories, 2016 and 2011 censuses". Statistics Canada. February 2, 2017. Retrieved April 30, 2017.
^ "Population by year of Canada of Canada and territories". Statistics Canada. September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 29, 2018.
^ Saskatchewanian is the prevalent demonym, and is used by the Government of Saskatchewan. According to the Oxford Guide to Canadian English Usage (
ISBN 0-19-541619-8; p. 335), Saskatchewaner is also in use.
^ "The Legal Context of Canada's Official Languages". University of Ottawa. Archived from the original on December 21, 2016. Retrieved October 7, 2016.
^ "Gross domestic product, expenditure-based, by province and territory (2015)". Statistics Canada. November 9, 2016. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
^ "Estimates of population, Canada, provinces and territories". Statistics Canada. December 18, 2013. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
^ "Statistics Canada, Quarterly demographic estimates, 2009". Statcan.gc.ca. December 23, 2009. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
^ "Midale Climate Normals 1971–2000". Environment Canada. Retrieved October 2, 2015.
^ "Yellow Grass Climate Normals 1971–2000". Environment Canada. Retrieved October 2, 2015.
^ abc "Treaty Land Entitlement – The English River Story, Saskatchewan" Archived July 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine., Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada, accessed November 25, 2011
^ "Government of Canada". Geonames.nrcan.gc.ca. September 18, 2007. Archived from the original on June 4, 2008. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
^ "Saskatchewan High Point". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved August 17, 2014.
^ Hydrology from The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan
^ "National Climate Data". Environment Canada. Archived from the original on January 19, 2012. Retrieved July 17, 2011.
^ Bray, Tim (December 23, 2008). "2008/12/23, Four PM". Retrieved February 28, 2008.English just doesn’t have words to describe cold of that intensity. I was appropriately dressed but am still a mild-climate West Coast Wimp, and the cold hurt me wherever it touched me; and it tried really hard to find chinks in my clothing's armor to penetrate and hurt.
^ "Average Weather for Saskatoon, SK – Temperature and Precipitation". Weather.com. July 29, 2010. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
^ "National Climate Data and Information Archive". Environment Canada. Retrieved September 2, 2010.
^ Houston, C. S.; Houston, S. (2000). "The first smallpox epidemic on the Canadian Plains: In the fur-traders' words". The Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases = Journal Canadien des Maladies Infectieuses. 11 (2): 112–115. PMC 2094753. PMID 18159275.
^ "Louisiana Purchase". Encyclopædia Britannica.
^ Howard A. Leeson (2001). Saskatchewan Politics: Into the Twenty-first Century. U of Regina Press. p. 116. ISBN 9780889771314.
^ Sandra Rollings-Magnusson, "Canada's Most Wanted: Pioneer Women on the Western Prairies." Canadian Review of Sociology and Anthropology 2000 37(2): 223–238; W. T. Easterbrook, Farm Credit in Canada 1938.
^ Peter Bush, Western Challenge: The Presbyterian Church in Canada's Mission on the Prairies and North, 1885–1925. (2000); Marjory Harper, "Probing the Pioneer Questionnaires: British Settlement in Saskatchewan, 1887–1914." Saskatchewan History 2000 52(2): 28–46. Issn: 0036-4908
^ Sandra Rollings-Magnusson, "Canada's Most Wanted: Pioneer Women on the Western Prairies." Canadian Review of Sociology and Anthropology (2000) 37#2: 223–238; E. Rowles, "Bannock, beans and bacon: An investigation of pioneer diet." Saskatchewan History, (1952) 1#1 pp. 1–16.
^ James M. Pitsula, "Disparate Duo" Beaver 2005 85(4): 14–24.
^ Arthur Henry Reginald Buller (1919). Essays on Wheat: Including the Discovery and Introduction of Marquis Wheat, the Early History of Wheatgrowing in Manitoba, Wheat in Western Canada, the Origin of Red Bobs and Kitchener, and the Wild Wheat of Palestine. pp. 218–20.
^ Ronald S. Love, "'A Harebrained Plan': Saskatchewan and the Formation of a Provincial Telephone Policy, 1906–1912." Saskatchewan History 2005 57(1): 15–33.
^ Kevin H. Burley, The Development of Canada's Staples 1867–1939: A Documentary Collection (1970) pp 139–43.
^ "Saskatchewan Stock Growers Association", Official Website
^ Girard Hengen, "A Case Study in Urban Reform: Regina Before the First World War." Saskatchewan History (1988) 41#1: 19–34
^ James M. Pitsula, For All We Have and Are: Regina and the Experience of the Great War (U of Manitoba Press, 2008), p 280. online review
^ Pitsula, For All We Have and Are p 41.
^ Lubomyr Luciuk, In Fear of the Barbed Wire Fence: Canada's First National Internment Operations and the Ukrainian Canadians, 1914–1920 (Kingston: Kashtan Press, 2001).
^ Archer, John H. (1996). "Regina: A Royal City". Monarchy Canada Magazine. Spring 1996. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved June 30, 2009.
^ "Government of Saskatchewan > About Government > News Releases > February 2002 > Province Honours Princess Margaret". Queen's Printer for Saskatchewan. February 11, 2002. Retrieved February 15, 2011.
^ "Royal couple touches down in Saskatchewan". CTV. May 18, 2005. Archived from the original on October 1, 2005. Retrieved June 30, 2009.
^ "Saskatchewan Ethnic Origins, Visible Minorities & Immigration" (PDF). Government of Saskatchewan.
^ The history of Saskatchewan's population from Statistics Canada
^ Canada's population. Statistics Canada. Retrieved September 28, 2006. Archived November 4, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Religions in Canada". 2.statcan.ca. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
^ "Canadian Food-Processing Sector". Invest in Canada. Archived from the original on October 14, 2010. Retrieved January 24, 2012.
^ Greuel, William. "Mustard". The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Retrieved January 9, 2017.
^ "Fact Sheet". Archived from the original on December 3, 2007. Retrieved January 16, 2009.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link) from the Saskatchewan Mining Association
^ Government of Saskatchewan. Oil and Gas Industry Archived September 29, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved on: April 26, 2008.
^ Government of Saskatchewan. The Saskatchewan Oil and Gas InfoMap. Retrieved April 26, 2008.
^ Gross domestic product, expenditure-based, by province and territory Archived April 20, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. from Statistics Canada
^ Public Accounts of Saskatchewan. Government of Saskatchewan. Retrieved March 25, 2017.
^ Government of Saskatchewan. "official page". Retrieved February 15, 2007.
^ "Saskatchewan One Room School House Project". SkSchool. Retrieved 2018-12-10.
^ "How Saskatchewan Health Pays Your Bill – Health – Government of Saskatchewan". Health.gov.sk.ca. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
^ abc French, Janet. (June 15, 2013) Half of women who want midwife turned away. Thestarphoenix.com. Retrieved on 2013-07-12.
^ "Saskatchewan Department of Highways and Transportation". Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ Saskatchewan Highways and Transportation. "Performance Plan – Saskatchewan Highways and Transportation". Retrieved September 4, 2007.
^ "Saskatchewan". World Travel Guide – Nexus Business Media. 2007. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved September 4, 2007.
^ "Canadian Pacific Railway". Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ Fung, K.I. (1969). "Atlas of Saskatchewan". Saskatoon: Modern Press.
^ Ivanochko, Bob (2006). "Bridges". CANADIAN PLAINS RESEARCH CENTER, UNIVERSITY OF REGINA. Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ abcdefghijkl "Saskatchewan City & Town Maps – Directory". Becquet's Custom Programming. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ "Airport History". Saskatoon Airport Authority. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ ab Chabun, Will (2006). "Aviation". CANADIAN PLAINS RESEARCH CENTER, UNIVERSITY OF REGINA. Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ Kraushaar, Clint (May 1998). "The RAF comes to Estevan". The Estevan Airport: A History to 1988. Estevan Community Access Project & Estevan Public Library. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ "Saskatchewan Airlines: Airlines in Saskatchewan, Canada". 1994–2008. Retrieved January 18, 2008.
^ Hon. Lawrence Cannon, M.P., P.C. Minister of transport, infrastructure and communities (2005–2008). "Statement by Hon. Lawrence Cannon, M.P., P.C. Minister of transport, infrastructure and communities at a news conference of Council of ministers responsible for transportation and highway safety". Newswire. CNW Group. Retrieved April 27, 2008.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ "NHL Players Born in Saskatchewan, Canada". Hockey-Reference.com. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
^ Chaput, John. "Hockey". The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
^ "Saskatchewan, The Home of Goal Scorers - Budweiser Canada". YouTube. Retrieved April 24, 2015.
^ Dept of the Secretary of State. Canada. (1984-01-01). The Arms, flags, and emblems of Canada. Deneau Publishers in co-operation with the Dept. of the Secretary of State and the Canadian Govt. Pub. Centre, Supply and Services Canada. p. 59. ISBN 9780888790309.
^ "Saskatchewan, flag of". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
^ "Walleye Wins Vote For Saskatchewan's Fish Emblem". Gov.sk.ca. September 30, 2005. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
^ Williams, G.D.V., R.A. Fautley, K.H. Jones, R.B. Stewart, and E.E. Wheaton. 1988. "Estimating Effects of Climatic Change on Agriculture in Saskatchewan, Canada." p. 219-379. In M.L. Parry et al. (ed.) The Impact of Climatic Variations on Agriculture. Vol. 1 Assessment in Cool Temperate and Cold Regions. Reidel Publ. Co. Dordrecht.
^ Riebsame. W.E. (1991). "Sustainability of the Great Plains in an Uncertain Climate."[permanent dead link]Great Plains Research Vol.1 No.1, University of Nebraska
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbeginfont-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ullist-style-type:none;margin-left:0.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>ddmargin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100font-size:100%
![]() Saskatchewan travel guide from Wikivoyage
Saskatchewan travel guide from Wikivoyage
- Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan
- Archer, John H. Saskatchewan: A History. Saskatoon: Western Producer Prairie Books, 1980. 422 pp.
- Bennett, John W. and Kohl, Seena B. Settling the Canadian-American West, 1890–1915. University of Nebraska Press, 1995. 311 pp.
- Waiser, Bill. Saskatchewan: A New History (2006)
- Bocking, D. H., ed. Pages from the Past: Essays on Saskatchewan History. Saskatoon: Western Producer Prairie Books, 1979. 299 pp.
- LaPointe, Richard and Tessier, Lucille. The Francophones of Saskatchewan: A History. Regina: University of Regina, Campion Coll., 1988. 329 pp.
- Lipset, Seymour M. Agrarian Socialism: The Cooperative Commonwealth Federation in Saskatchewan: A Study in Political Sociology. University of California Press, 1950.
- Martin, Robin Shades of Right: Nativist and Fascist Politics in Canada, 1920–1940, University of Toronto Press, 1992.
Porter, Jene M (2008). Perspectives of Saskatchewan. University of Manitoba Press. ISBN 978-0-88755-183-3.
Veldhuis, Niels (2009). "Saskatchewan Prosperity: Building on Success". Fraser Institute.
- Grams, Grant W.: Der Volksverein deutsch-canadischer Katholiken, the rise and fall of a German-Catholic Cultural and Immigration Society, 1909-1952, in Nelson H. Minnich (ed.) The Catholic Historical Review, 2013.
- Grams, Grant W.: Deportation from Saskatchewan during the Great Depression, the case of H.P. Janzen, in John D. Thiesen (ed.), Mennonite Life, 2010.
- Grams, Grant W.: The Deportation of German Nationals from Canada, 1919 to 1939, in Peter S. Li (ed.), Journal of International Migration and Integration, 2010.
- Grams, Grant W.: Immigration and Return Migration of German Nationals, Saskatchewan 1919 to 1939, in Patrick Douand (ed.), Prairie Forum, 2008.
- Grams, Grant W.: Was Eckhardt Kastendieck one of Saskatchewan’s most active Nazis?, in Jason Zorbas (ed.), Saskatchewan History, 2007.
External links
- Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan at Curlie- Royal Canadian Mounted Police
- SaskTourism
- Saskatchewan History Online
Coordinates: 55°N 106°W / 55°N 106°W / 55; -106



